
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
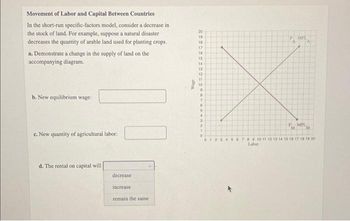
Transcribed Image Text:Movement of Labor and Capital Between Countries
In the short-run specific-factors model, consider a decrease in
the stock of land. For example, suppose a natural disaster
decreases the quantity of arable land used for planting crops.
a. Demonstrate a change in the supply of land on the
accompanying diagram.
b. New equilibrium wage:
c. New quantity of agricultural labor:
d. The rental on capital will
decrease
increase
remain the same
Wage
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
0
5
4
3
2
1
0
P MPL
A A
MPL
01234 678 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Labor
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- q12arrow_forwardIn the long run, a perfectly competitive firm makes O A) either a positive economic profit or a normal profit. B) zero accounting profit. C) zero economic profit. D) negative economic profit, that is, an economic loss. E) a positive economic profit.arrow_forwardIf a person's wage decreases: A) his marginal value product curve will shift to the left B) his marginal calue product curve will shift to the right C) there will be a movement to the northwest along the marginal value product curve D) the slope of the marginal value product curve will increasearrow_forward
- B and c pleasearrow_forward● Suppose government mandates required firms to make 'safety expenditures' on behalf of workers that did not improve labor productivity. Describe the scale and substitution effects these mandates would have in the labor market.arrow_forwardAssume a firm is trying to maximize output subject to a budget and is currently in the long run equilibrium shown below. Make changes to the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the wage. Make sure that the graph shows the new output-maximizing combination as well as the new levels labor and capital.arrow_forward
- 1. Consider a static labour supply model for an individual. Assume that the person works a positive number of hours. Assume that the utility function is of the following form: U=x0.5 +8(T-h)(0.5) where x is consumption and his hours of work, and 8 is a parameter of the utility function. The person is paid a wage of w for each hour worked. The person has no other source of income other than employment earnings. Assume that the price of x equals 1. a) Specify the utility maximization problem, write down the Lagrange function, and solve for the first order conditions. b) Solve for the MRS condition between consumption and hours of work. c) Assume that 8=2 if the person has a child living at home, and 8=1 otherwise. Explain (and either show mathematically or graphically) how this will affect the optimal number of hours of work of the person.arrow_forwardWhat do economists mean by "deminishing returns" to an input? What causes diminishing returns? Where would one observe this principle at a job and the real world?arrow_forward38) In the short run, the marginal product of labor might increase initially as more workers are hired because A) the first workers hired get to use the best equipment. B) specialization allows a worker to focus on one task, thereby increasing her proficiency at that task. c the best workers are hired first and later hires are not as skillful. Dj beyond some point, a firm has hired too many workers.arrow_forward
- = $30 and wage rate Let the production function be given by: q = 10(L^2)K, with rental rate v W = $20. 1. How much K and L are employed to produce 11,250 units of output? 2. Suppose that the firm wants to increase output to 19, 440 units of output, now how much K and Lare employed to produce with minimize cost? 3. Suppose that in the short run the amount of capital is fixed at K = 10, what is the firm short run fixed cost? 4. Suppose that in the short run the amount of capital is fixed at K = 10, what is the short run total cost of producing 900 units of output?arrow_forwardConsider the labor–leisure budget constraint curve on the graph. This curve shows trade‑offs between income and leisure that must be made over the course of one week. Assume there are no artificial barriers to limits on hours worked and that the wage is $25 per hour. Determine the vertical and horizontal intercepts. vertical intercept: $ horizontal intercept: harrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education