
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
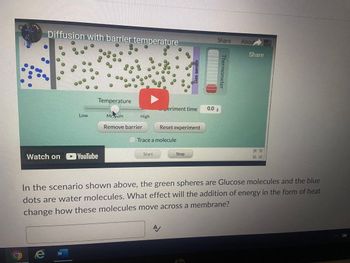
Transcribed Image Text:Diffusion with barrier temperature
1.
000
Low
Watch on YouTube
W
8
O
**,
Temperature
MATUM
...
Remove barrier
00
High
208
Start
O
Trace a molecule
A
periment time
Gas sensor
Reset experiment
Stop
Share
0.0 s
Thermometer
About
Share
In the scenario shown above, the green spheres are Glucose molecules and the blue
dots are water molecules. What effect will the addition of energy in the form of heat
change how these molecules move across a membrane?
Ra
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- which of the following changes in the plasma membrane of a salmon is most likely to occur as it migrates to a much colder region of the Pacific Ocean? HInt: the fluidity of the salmon's plasma membranes must remain relatively constant during its migration. The percentage of integral membrane proteins in the plasma membrane would increase The percentage of unsaturated fatty acid tails in plasma membrane phospholipids would increase The percentage of unsaturated fatty acid tails in plasma membrane phospholipids would decrease The percentage of peripheral membrane proteins in the plasma membrane would increasearrow_forwardb) If you soak an animal cell that is permeable to both water and glucose in either 5.5% glucose or 0.9% NaCl (both isosmotic solutions), the cell exposed to 5.5% glucose will gain water, while the cell exposed to 0.9% NaCl will not gain water. Predict why this is the case.arrow_forwardYou have a beaker filled with a solution containing 2M glucose, 4M urea and 1M salt.Suspended in the solution is a cell that containing a solution of 1M glucose, 8M urea and 3Msalt. The membrane of the cell is permeable to glucose and salt but not urea. Answer each of thefollowing questions:a. Where will water move?b. Where will urea move?c. Where will glucose move?d. Where will salt move?e. What will happen to the volume of fluid inside the cell?f. What will happen to the osmolarity of the fluid inside the cell?arrow_forward
- In the experimental conditions described below, how many molecules of dextrose do you have to add to the extracellular fluid in order to make it iso-osmotic relative to the intracellular fluid? Intracellular fluid: Number of water molecules = 60 • Number of Dextrose molecules = 7 • Number of Sucrose molecules = 3 ● Extracellular fluid: • Number of water molecules = 160 • Number of dextrose molecule = ???? • Number of Sucrose molecules = 0arrow_forwardWhat molecules are found in animal cell membranes, but not in plant cell membranes? please explain.arrow_forwardConsider the artificial cell experiment below: Lactose = 2.0 M Ca+ = 0.4 M The ion channels in the membrane will allow Ca+ to pass freely, but nothing else. The starting conditions for the experiment are shown. Lactose = 0.1 M Ca+ = 3.0 M Rewrite the following statement to make it correct: "Eventually, there will be a net movement of water out of the cell because the inside of the cell is hypotonic compared to the environment." Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt ✓ Paragrapharrow_forward
- Shown below are cells (colored) that were recently placed into a beaker containing a clear solution For each scenario, indicate whether movement of the molecule into the cell will occur using facilitated diffusion or active transport. А. B. 125mM 20mM fructose glucose 85MM 35mM fructose glucose OA= facilitated diffusion; B= facilitated diffusion OA= active transport; B= active transport O A= active transport; B= facilitated diffusion A= facilitated diffusion; B= active transportarrow_forwardIn conditions of dehydration, plant cells can increase their water retention by regulating the function of some or all of their aquaporins, membrane-bound protein channels that allow water to move through the cell membrane via facilitated diffusion. Which of the following describes a likely mechanism by which aquaporins can be used to regulate the movement of water across the plant cell membrane? A B с D Synthesis of additional aquaporins by the plant cell ribosomes will allow the cell to coun- teract the movement of water out of the cell. Inhibition of ATP hydrolysis will make the aquaporins unable to remove water from the cell and cause more water to remain in the cell. Inactivation of aquaporins will make water molecules unable to move across the plant cell membrane and allow more water to remain in the cell. Inhibition of the plant cell Golgi apparatus will decrease the production rate of vesicles and slow down the exocytosis of water molecules.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON