
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
This is a review question not a test
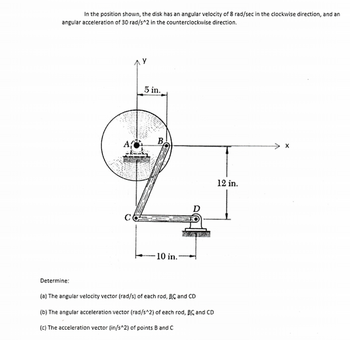
Transcribed Image Text:In the position shown, the disk has an angular velocity of 8 rad/sec in the clockwise direction, and an
angular acceleration of 30 rad/s^2 in the counterclockwise direction.
y
5 in.
B
-10 in.:
D
12 in.
Determine:
(a) The angular velocity vector (rad/s) of each rod, BC and CD
(b) The angular acceleration vector (rad/s^2) of each rod, BC and CD
(c) The acceleration vector (in/s^2) of points B and C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The crank link AB of the crank and slider mechanism has an angular velocity of WAB = 6 rad/s and an angular acceleration of a = 2 rad/s", both directed counterclockwise. The distances shown are hi = 6 in, h2 = 8 in and di 6 in. Also, a = 8, 6 = 15 %3D and c = 17. h2 WAB dAB What is the absolute value of the magnitude of the velocity of Point C at the given instant? vc =| in/s What is the absolute value of the linear acceleration of Point C at the given instant? in/s асarrow_forwardBar AB is pin-supported at A and attached to bar BC. The end of bar BC is connected to the slider block C. At the instant shown, the angular velocity of bar BC is 0.5625 rad/s counterclockwise, and the acceleration of point B is 1.125 m/s^2 downward. Find the following: a. Angular speed of bar AB b. Angular acceleration of bar AB c. Angular acceleration of bar BC d. Acceleration of slider block C 50 4 3 C 0.5 m B 2.0 m Aarrow_forward+ G In the above diagram, the wheel starts from rest and rolls without slipping. The force (you don't need the value) causes a constant angular acceleration of 7.112 rad/s2. The radius of the wheel is R - 0.392 m. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the point at the top of the wheel at time t 1.400 s? This is the point at the outer edge directly above the center of gravity, Gwhere the force F connects to the wheel. Use units of m/s. Don't place units in your answer, 3 oarrow_forward
- The following diagram shows a piston moving in a cylinder with rod AB. Point B is rotating clockwise with an angular velocity of w. cylinder piston A connecting rod crank bearing B ResearchGate The motion of B is given by the equation r = C cos(wt) + Dsin(wt) Were r is the horizontal +vertical distance of B from O, and C, D are constants. For C=D=42mm and w = 20 rad/s. (i) Write r in the form Rcos (wt ± ß) and state the amplitude and period of r. (ii) Sketch one complete cycle of r. (iii) Explore the differences between the derived form and drawn formarrow_forward4. A wheel having a diameter of 30cm starts from rest and accelerates uniformly to an angular velocity of 900 rpm is 5 sec. Find the position at the mo end of 1sec of a point originally on top of the wheel. ANS: at the bottom 5. A flywheel of radius 30cm starts from rest and rotates with constant angular acceleration of 0.5 rad/s2. Compute the total acceleration of the point on the rim after it has turned through 120°. ANS: 0.65 m/sarrow_forward8. The constant angular acceleration of the rotating disk is 12 rad/s2. The angular velocity of the disk is 24 rad/s clockwise when t = 0. Determine the total angle turned by the disk between t = 0 and t = 4sec. ANS: 48 rad 9. The angular acceleration ?, rad/s^2 of a rotating disk is related to its angular velocity ?, rad/s by ? = 4 √?. When t = 0, the disk is at rest and the angular position coordinate of a line in the disk is θ = 8rad. Find the expression for θ(?). ANS: θ(?) = 0.1667 ?^1.5 + 8 10. The rotation of a wheel is defined by the relation, θ = 3t^3 – 5t^2 + 7t – 2 where θ is in radian and t in seconds. Find the angular acceleration when t = 3 seconds. ANS: 44 rad/s^2 12. The shaft of a motor turns at constant speed of 3000 rpm. It turns to how many radians in 40 seconds. ANS: 12566.37 rad 13. The motor driving a grindstone is switched off when the latter has a rotational speed of 240 rpm. After 10sec, the speed is 180 rpm. If the angular retardation remains constant, how…arrow_forward
- For the diagram below the angular velocity of the wheel is w = 2rad/s. The location of the instantaneous center of zero velocity is at point 0.3 m OD 1.2 m OB 45% O somewhere not listed in the other options. OC 0.3 m Carrow_forwardThe figure as shown below is a rigid body undergoing planar motion. The absolute tangential accelerations of the points R and S on the body are 150 mm/sec2 and 300 mm/ sec2 respectively in the directions shown. What is the angular acceleration of the rigid body? Al 10 mm 10 mm 90 mm (a) 1.66 rad/ sec2 (b) 3.33 rad/ sec2 (c) 5.00 rad/ sec2 (d) 2.50 rad/ sec2 In the mechanism ABCD shown in the given figure, the fixed link is denoted as (1), Crank AB as (2), rocker BD as (3), Swivel trunnion at C as (4). The instantaneous centre I41 is at (a) the centre of swivel trunnion. (b) the intersection of line AB and a perpendicular to BD to (c) Infinity along AC (d) Infinity perpendicular to BD. wwwarrow_forwardA ball bearing is moving radially outward in a slotted horizontal disk that is rotating about the vertical z axis. At the instant shown in figure below, the ball bearing is 3.6 in from the center of the disk. It is traveling radially outward at a velocity of 4.4 in/sec relative to the disk and has a radial acceleration with respect to the disk of 5.3 in/sec? outward. What does the magnitude of 0 (in rad/s2) have to be for the ball bearing to have a total acceleration of zero? Figure is from "Engineering Mechanic An Introduction to Dynamics", McGill and King.arrow_forward
- If a car is travelling along a straight road at 13.4 ms-1 and the linear speed of a point in the tyre is relative to the centre of the wheel making it 13.4 ms-1 too, and the radius of from the centre of the wheel to the tyre tread is 0.240 m, what is the angular speed of each tyre and what is the direction of the angular velocity vector of each wheel point in relation to the direction of the forward motion of the car?arrow_forwardA four-bar linkage is shown in the figure (the ground "link" OC is considered the fourth bar). If the angular velocity and angular A four-bar linkage is shown in the figure (the ground "link" OC is considered the fourth bar). If the angular velocity and angular acceleration of drive link OA are 6.1 rad/s and 6.6 ras/s^2 respectively, both counterclockwise, determine the angular accelerations of bars AB and BC for the instant represented. The angular accelerations are positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise. The answers are not: aAB= 2.356 and aBC = 11.327 or 390.82 and 465.7arrow_forwardA ball bearing is moving radially outward in a slotted horizontal disk that is rotating about the vertical z axis. At the instant shown in figure below, the ball bearing is 2.5 in from the center of the disk. It is traveling radially outward at a velocity of 3.9 in/sec relative to the disk and has a radial acceleration with respect to the disk of 5.9 in/sec? outward. What does the magnitude of 0 (in rad/s) have to be for the ball bearing to have a total acceleration of zero? Figure is from "Engineering Mechanic An Introduction to Dynamics", McGill and King.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY