
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
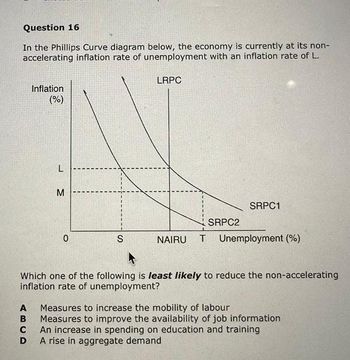
Transcribed Image Text:Question 16
In the Phillips Curve diagram below, the economy is currently at its non-
accelerating inflation rate of unemployment with an inflation rate of L.
Inflation
(%)
ABCD
L
M
0
S
LRPC
SRPC2
SRPC1
NAIRU T Unemployment (%)
Which one of the following is least likely to reduce the non-accelerating
inflation rate of unemployment?
Measures to increase the mobility of labour
Measures to improve the availability of job information
An increase in spending on education and training
A rise in aggregate demand
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Phillips curve in Lowland takes the form of π = 0.04 − 0.6(u − 0.05), where π is the actualinflation rate and u is the unemployment rate. The Phillips curve in Highland takes the form ofπ = 0.08 − 0.4(u − 0.05). The current unemployment rate in both countries is 9 percent (0.09). For both countries, analyze the impact on inflation of a 2% decrease in unemployment? In which country will policymakers face a bigger trade-off if they try to reduce unemployment in the shortrun? Whyarrow_forwardAssume that a 1% change in the inflation rate causes a 1% increase in nominal interest rates, which in turn causes a 1% drop in real growth the following year. During the latter half of the 1990s, real growth averaged about 4%. Calculate how much inflation would have to increase for the following to happen, using Okun’s Law. (A) A 1% increase in the unemployment rate. (B) A big enough change to cause a ‘‘typical’’ recession, where real GDP declines 2%. (C) Suppose real growth slows down to 2½% because of a change in consumer and business sentiment. How much would the unemployment rate change each year?arrow_forwardConsider an economy with a natural unemployment rate, u, of 9%. The x = x - 2(u - ū) Assume that Okun's Law holds so that a 1 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate maintained for one year réduces GDP by 2% of full employment output. Note: Okun's Law can be expressed as: Y-Y expectations-augmented Phillips curve is: = -2(u - u) a. Consider a two-year disinflation. In the first year actual inflation, , is 13% and expected inflation, xº, is 17%. What is the first year unemployment rate? % (Enter your response as a percentage rounded to one decimal place)arrow_forward
- Suppose that in a population of 200 million persons, 150 million are in the labor force and 120 million are employed. Then the unemployment rate for this economy is: A) 20 percent B) 40 percent C) 60 percent D) 80 percentarrow_forwardIn each of the following scenarios, indicate which parameter in the Search and Matching Model of Unemployment might change in that scenario and why and whether it will increase or decrease. Using the two graphs outlined in the Notes on Search and Matching unemployment, indicate what happens to the Beveridge, Definition, WS, and JC curves (in both a wage-tightness graph and a vacancies-searchers graph) and steady state θ, w, v and s in response to the change in the parameter. State in words which curve shifts and in what direction and what happens to the steady state equilibrium variables. Drawing a graph is desirable but not necessary. a. The appearance of LinkedIn.com allows employers to post open positions on the webstie and to find suitable workers to hire faster. b. Sectoral shifts in the economy become more frequent so that different jobs (industries) are destroyed more often.arrow_forwardPlease show me step-by-step explanations, please. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Which of the following would impact the Natural Rate of Unemployment? Question 7 options: All Answer Options A penalty fee for businesses that fire or layoff workers A workplace safety policy that raises business operation costs The availability of job informationarrow_forwardSuppose there are 180 million employed people and 20 million unemployed people. a) What is the unemployment rate? b) Suppose that 5 million unemployed people give up their search for jobs and become discouraged workers. What is the new official unemployment rate?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Do not round any of your answers. Steady-State Unemployment Problem Suppose the rate of job finding (a) is 0.357, while the rate of job separation (B) is 0.018. If there are 100,000 people in the (fixed) labor force and 5,000 of them are unemployed, the unemployment rate is currently equal to percent. Given the values for a and B, the number of people who find a job this month will equal and the number of people who lose or leave a job this month will equal Because there are (more/fewer) people finding a job than losing or leaving one, the rate of unemployment is expected to change until it reaches the steady-state equilibrium value ofarrow_forwardUse the FRED database (https://fred.stlouisfed.org/) to find out what happened to theprice of oil (WTISPLC) and the New Zealand unemployment rate(LRUNTTTTNZQ156S) in 2022. What does our model of labour marketdetermination predict will happen to the natural unemployment rate when oil pricesincrease? What is the consequence for inflation given these developments, and why(Be careful to distinguish between the natural and actual unemployment rate)arrow_forwardSuppose that Julie is laid off because she works at the last automobile manufacturer in Virginia, which has just closed. Julie makes $30 per hour because of her skills in auto making. However, the closest places Julie can relocate to which require that skill are Texas, Mississippi, or Michigan. Because she takes care of her elderly mother, she cannot move. Which of the following types of unemployment is she experiencing?Give reason Group of answer choices Frictional unemployment Cyclical unemployment Structural unemployment Demand-pull unemploymentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education