
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
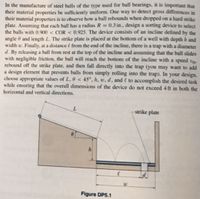
Transcribed Image Text:In the manufacture of steel balls of the type used for ball bearings, it is important that
their material properties be sufficiently uniform. One way to detect gross differences in
their material properties is to observe how a ball rebounds when dropped on a hard strike
plate. Assuming that each ball has a radius R = 0.3 in., design a sorting device to select
the balls with 0.900 < COR < 0.925. The device consists of an incline defined by the
angle ở and length L. The strike plate is placed at the bottom of a well with depth h and
width w. Finally, at a distance & from the end of the incline, there is a trap with a diameter
d. By releasing a ball from rest at the top of the incline and assuming that the ball slides
with negligible friction, the ball will reach the bottom of the incline with a speed to.
rebound off the strike plate, and then fall directly into the trap (you may want to add
a design element that prevents balls from simply rolling into the trap). In your design,
choose appropriate values of L, 0 < 45°, h, w, d, and e to accomplish the desired task
while ensuring that the overall dimensions of the device do not exceed 4 ft in both the
horizontal and vertical directions.
strike plate
Figure DP5.1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please provide the correct answer choicearrow_forward3) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): DO Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0 = 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R = 0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u=0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: →→V=Ro=0.075 x 14.28 = 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 x 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward5) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0= 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R = 0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u = 0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: →V=Roo= 0.075 x 14.28 = 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 x 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward
- 40. A tensile test specimen has a gage length 2.0 in and diameter 0.875 in. Yielding occurs at a load of 35,500 lb. The corresponding gage length 2.0113 in (neglect the 0.2 percent yield point). The maximum load of 45,000 lb is reached at a gage length 2.543 in. If the specimen necked down to a diameter 0.765 in, determine the percent reduction in area (round to the nearest whole %)arrow_forwardIf the wrought stock material costs $60 per kg, what is the lost value due to the material removed, assuming scrap is sold for $3 per kg? Assume the density of titanium is 4.5 g/cm3. Briefly explain how you got your answer. Neglect costs of lubricant/coolant, chip handling, etc. Round your answer down to the nearest dollar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY