
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
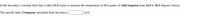
Transcribed Image Text:In the laboratory a student finds that it takes 21.8 Joules to increase the temperature of 13.1 grams of solid tungsten from 24.9 to 38.3 degrees Celsius.
The specific heat of tungsten calculated from her data is
J/g°C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemist carefully measures the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 567.0 mg sample of C,H,F, from 2.6 °C to 16.8 °C. The experiment shows that 11.6 J of heat are needed. What can the chemist report for the molar heat capacity of C,H,F,? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 9. 4'2 J-mol 1 1 •K x10arrow_forwardAn experiment was conducted to determine the specific heat of platinum. It was determined that 158.8 Joules of heat were required to increase the temperature of a 50.0 gram sample of platinum from 20.0 oC to 45.5 oC. Based on these experimental results calculate the specific heat (J/goC) of platinum. Do not type units into your answer.arrow_forwardthe laboratory a student finds that it takes 101 Joules to increase the temperature of 13.6 grams of solid iodine from 20.6 to 39.3 degrees Celsius. e specific heat of iodine calculated from her data is J/g°C.arrow_forward
- You discover a new substance and wish to determine its specific heat capacity. Your sample weighs 229 g and upon absorbing 16.4 kJ of heat the temperature is raised from 19.6K to 53.7K. What is the specific heat capacity (in J/g•K) of the metal?arrow_forwardAn experiment was conducted to determine the specific heat of platinum. It was determined that 158.8 Joules of heat were required to increase the temperature of a 50.0 gram sample of platinum from 20.0 oC to 45.5 oC. Based on these experimental results calculate the specific heat (J/g⋅⋅oC) of platinum.arrow_forwardA piece of solid substance weights 4.0 g, and requires 150 J to increase its temperature from 30.0 degrees Celsius to 40.0 degrees Celsius. What is the specific heat capacity of the substance?arrow_forward
- 10 A student heats 84.17 mL of water to 95.27°C using a hot plate. The heated water is added to a calorimeter containing 73.92 mL of cold water. The water temperature in the calorimeter rises from 2.15°C to 37.48°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J and the density of water is g. °C 1.00 mL Assuming that heat was transferred from the hot water to the cold water and the calorimeter, determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. J Heat capacity of calorimeter = °Carrow_forwardThe burning of 28g of vegetable cause the temperature of 58.18 g of water in a soda can calorimeter to increase from 21.5°C to 28.1 Calculate the amount of heat absorbed by the water using the specific heat of water at 4.18 J/gºC.arrow_forwardIf 30.5 g of LiBr are dissolved 350.0 g of water at 20.0 °C in an insulated container, a temperature change is observed. The Δ H of solution of LiBr is -48.8 kJ/mol. Assuming that the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/(g C) and that no heat is gained or lost by the container, what will be the final temperature of the solution?arrow_forward
- A chemist carefully measures the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 0.46 kg sample of a pure substance from 36.2 °C to 51.6 °C. The experiment shows that 33. kJ of heat are needed. What can the chemist report for the specific heat capacity of the substance? Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardIn the laboratory a student finds that it takes 145 Joules to increase the temperature of 14.7 grams of solid silicon from 23.0 to 38.0 degrees Celsius. The specific heat of silicon calculated from her data is J/g°C.arrow_forwardA chemist carefully measures the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 639.0 g sample of C,H,N from -8.7 °C to 6.7 °C. The experiment shows that 2.60 × 10* J of heat are needed. What can the chemist report for the molar heat capacity of C,H,N? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. - 1 ·K J• mol х10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY