
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
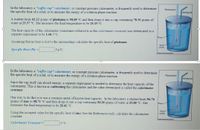
Transcribed Image Text:In the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine
the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction.
Thermometer
Stirring rod
A student heats 62.12 grams of platinum to 98.69 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 78.31 grams of
water at 23.37 °C. She measures the final temperature to be 25.15 °C.
The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a
separate experiment to be 1.66 J/°C.
Water
Assuming that no heat is lost to the surroundings calculate the specific heat of platinum.
Metal
sample
Specific Heat (Pt) =|
Jg°C.
2es T sCole
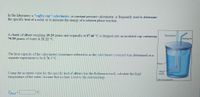
In the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine
the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction.
Thermometer
Stirring rod
Since the cup itself can absorb energy, a separate experiment is needed to determine the heat capacity of the
calorimeter. This is known as calibrating the calorimeter and the value determined is called the calorimeter
constant.
One way to do this is to use a common metal of known heat capacity. In the laboratory a student heats 96.76
grams of zinc to 98.71 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 80.20 grams of water at 20.80 °C. She
measures the final temperature to be 28.61 °C.
Water
Using the accepted value for the specific heat of zinc (See the References tool), calculate the calorimeter
Metal
sample
constant.
The nBrekC
Calorimeter Constant = |
J/°C.
Transcribed Image Text:In the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine
the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction.
A chunk of silver weighing 19.29 grams and originally at 97.46 °C is dropped into an insulated cup containing
79.59 grams of water at 21.22 °C.
Thermometer
Stirring rod
The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a
separate experiment to be 1.76 J/°C.
Water
Metal
sample
Using the accepted value for the specific heat of silver (See the References tool), calculate the final
temperature of the water. Assume that no heat is lost to the surroundings.
2000 Thomaon-Brocks/Cole
Tfinal =
°C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fundamentals%20and%20Applications%206th%... nt 7- ng ed eat ? hed The 0°C. 2 m is e. If satu- heat unit 10-15 Water is to be boiled at atmospheric pressure in a mechanically polished steel pan placed on top of a heating unit. The inner surface of the bottom of the pan is maintained at 110°C. If the diameter of the bottom of the pan is 30 cm, determine (a) the rate of heat transfer to the water and (b) the rate of evaporation. prt sc F10 FIGURE P10-15 WH XH home F11 000⁰ end P17 665 CHAPTER 10 Desktop insert 23°C delete Settings in tow ONDENG CE 6:07 PM 19/12/2022 +/-arrow_forwardhow to draw and label a process flowchartarrow_forwardI don’t understand thisarrow_forward
- A fully charged battery contains 0.02 kmol Ag₂O (silver oxide) and 0.02 kmol Zn (zinc). The battery is initially at a temperature of 21°C. The fully charged battery is then discharged for half an hour under adiabatic conditions (no heat leaves the system). During the half hour of being discharged, the electric current from the battery does 200 kJ of work external to the battery system (none of this external work heats the battery). During this half hour, 0.001 kmol of both reactants are consumed in the net cell discharge reaction: Please see the following table for heat capacities and heats of formation. The heats of formation below show the amount of energy (kJ) needed to form one kmole of each component. If the heat of formation is negative, then forming that species releases energy (to do work or provide heat). Therefore, to create one kmole of silver oxide 29000 kJ energy is released and is generated in the battery (for work or heat), and if one kmole of silver oxide decomposes…arrow_forward6. A 15.0 gram sample of silver metal is heated to 96.7∞C and then dropped into 55.0 grams of water at 23.0∞C. Assuming that all the heat lost by the silver is absorbed by the water, calculate the final temperature of the silver and waterarrow_forwardIn the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction. A student heats 63.46 grams of aluminum to 97.86 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 76.65 grams of water at 22.09 °C. She measures the final temperature to be 33.20 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.66 J/°C. Assuming that no heat is lost to the surroundings calculate the specific heat of aluminum. Specific Heat (Al) = = J/g °C. Water- Thermometer Metal- sample 2003 Thomson-Brooks/Cole Stirring rodarrow_forward
- You work in a chemical plant which recovers gold from gold-plated electrical connectors using heated (Tacid = 55oC) nitric acid. Once the acid is “used up” it gets piped through the plant to a separate facility for disposal. During that time, it passes through a cooling chamber to strip the waste heat off the acid for recovery. The acid passes through the chamber in 6m long, 400mm OD, 360mm ID aluminum tubes. The chamber passes room-temperature air over the tubes at 8 m/s. Approximately 0.45 cubic meters of acid is processed per hour. a) What is the Reynold’s number of the nitric acid passing through the tube? Is it turbulent or laminar? b) What is the heat transfer coefficient of the nitric acid to the inside of the aluminum tube? c) What is the heat transfer coefficient of the air over the tube? d) What is the overall heat rate from the nitric acid to the air? e) Based on your answers here, in a gas-liquid heat exchanger, which side of the exchanger are the fins usually on?…arrow_forwardQ3(a) A stream of benzene vapor at 580 °C and 1 atm is cooled and converted to a liquid at 25 °C and latm in a continuous condenser. (i) (ii) Illustrate a completely process path for the above process. Calculate the total enthalpy change for this process.arrow_forwardMagnesium metal, a gray solid, is heated in a crucible in the presence of oxygen. A white powder is collected from the crucible. This is an example of A) a chemical change B) a separation C) a mixture D) a physical changearrow_forward
- A CHM student completing the calorimetry experiment mixes 20.0 mL of 1.10 M HCl (aq) with 20.0 mL of 1.05 M NaOH (aq), and observes the temperature increase of 6.611∘∘C. Assume that the density of each solution is 1.02 g/mL, and the specific heat for the resulting solution is 4.02 J/g∙℃. Calculate the change in enthalpy for this reaction (ΔHrxn) in kJ/mol H2O. Use the correct sign (+ or -) and significant figures.arrow_forwardA bomb calorimeter, or constant volume calorimeter, is a device often used to determine the heat of combustion of fuels and the energy content of foods.arrow_forwardMETAL Suppose you heat a metal object with a mass of 32.9 g to 96.6 °C and transfer it to a calorimeter containing 100.0 g of water at 17.2 °C. The water and metal reach a final temperature of 22.4 °C. What is the specific heat of the metal in J/g-°C?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The