
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
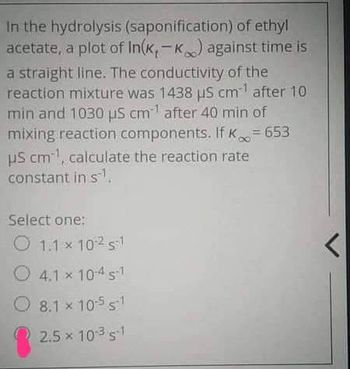
Transcribed Image Text:In the hydrolysis (saponification) of ethyl
acetate, a plot of In(k,-k) against time is
a straight line. The conductivity of the
reaction mixture was 1438 μS cm after 10
min and 1030 μS cm after 40 min of
mixing reaction components. If K∞ = 653
US cm, calculate the reaction rate
constant in s.
Select one:
1.1 × 10251
x
4.1 × 10-4 s1
8.1 x 10-5 51
2.5 × 10-3 s-1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What are the benefits of measuring the initial rate of a reaction Vå for use in kinetic studies? (This is a multi-select question). [ES] can be measured accurately. changes in [S] are negligible, so the value of [S] is known. changes in Km are negligible, so Km can be treated as a constant. V₁ = Vmax. --> A negligible amount of product has formed, so that the back reaction P -- need not be considered. ESarrow_forwardDirect methanol fuel cells (DMFCS) have shown some promise as a viable option for providing "green" energy to small electrical devices. Calculate E° for the reaction that takes place in DMFCS: CH3OH(I) + 3/2 02(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H20(1) Use the following values. AG°H,0(1) = -237 kJ/mol AG°O2(g) = 0 kJ/mol AG°CO2(9) = -394 kJ/mol AG°CH3OH(I) = -166 kJ/mol. E° = Varrow_forwardWhat is the likely keq for an enzyme that has a deltaG =-18.3kj/mol?arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction: Glucose 6-phosphate + Glucose 1-phosphate After reactant and product were mixed and allowed to reach equilibrium at 25C, the concentration of each compound was measured: (Glucose 1-phosphate] - 0.002 M [Glucose 6-phosphate 0.05 mM Calculate the Keg and the AG knot prime (e.g. standard free energy change). O Keg- 40: AG knot prime 9.14 kJ/mol O Ken- 19: AG knot prime -7.3 kJ/mol O Keg" 0.04: AG knot prime-7.98 kJ/mol Kea 4: AG knot prime -914 kJ/mol O Keg 40: AG knot prime - 9.14 k/molarrow_forwardIf glucose, phosphate, and glucose-6-phosphate arecombined in concentrations of 4.8, 4.8, and 0.25 mM,respectively, what is the equilibrium constant for thehydrolysis of glucose-6-phosphate at a temprature of258C?arrow_forwardFrom a kinetics experiment, Kcat was determined to be 55sec^-1. For the kinetic assay, 0.05mL of a 0.05mg/mL solution of enzyme was used, and the enzyme has a molecular weight of 30,000g/mole. Assume a reaction volume of 3mL. Calculate Vmax (um*min^-1) for the enzyme and catalytic efficiency (in M^-1sec^-1) for the enzyme. The Km for the enzyme was determined to be 8.3*10^-2M.arrow_forward
- A particular reaction has ΔH°' = 1 kJ mol-1 and ΔS°' = -104 J mol-1 K-1. Calculate the value of ΔG°' in kJ mol-1 at 25.0 °C.arrow_forwardA biochemist is trying to determine the type of proteases they have isolated from walrus blubber. The three proteases and their relative activities in the presence of the indicated non-specific irreversible inhibitors are shown in the table below: Protease a Protease B Protease y Given this data, please answer the following question: The catalytic site of Protease ß contains an important: C R H + lodoacetate Normal Activity Normal Activity No Activity U + Tetranitromethane Normal Activity No Activity Normal Activityarrow_forwardThe Ksp values of silver chromate Ag2CrO4 and silver iodate Ag(IO3) are given below. Ag2CrO4 Ag(IO3) Ksp 1.12 x 10-12 3.17 x 10-8 Based on these Ksp values, which of the following is true? Choose one option only. Options: a. In the solution consisting of 1.00 x10-4 M Ag+ and 5.00 x10-5 M CrO42-, Ag2CrO4 precipitate will form. b. In the solution consisting of 1.0 x10-4 M Ag+ and 1.0 x10-4 M IO3-, Ag(IO3) precipitate will form. c. In pure water, the solubility of Ag2CrO4 is lower than the solubility of Ag(IO3). d. In the solution consisting of 0.200 M CrO42- and 0.200 M IO3-, Ag2(CrO4) will precipitate first if we add Ag+ ions gradually into the above mixture.arrow_forward
- Sodium carbonate is a reagent that may be used to standardize acids in the same way that you have used KHP in this experiment. In such a standardization it was found that a 0.498 -g sample of sodium carbonate required 21.7mLmL of a sulfuric acid solution to reach the end point for the reaction. Na, CO, (aq) + H₂SO (aq) - H₂O(l) + CO₂ (g) + Na SO (ag) What is the molarity of the H, SO? 2 3 2 4 2 2 2 2 4 Sodium carbonate is a reagent that may be used to standardize acids in the same way that you have used KHP in this experiment. In such a standardization it was found that a 0.498-g sample of sodium carbonate required 21.7 mL mL of a sulfuric acid solution to reach the end point for the reaction. Na2CO3(aq) + H2SO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2 (g) + Na2SO4(aq) What is the molarity of the H2SO4? ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer ? Marrow_forwardA galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn(aq) +Ba(s) → Sn (s) + Ba** (aq) 2+ 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 7.71 M Sn in one half-cell and 5.89 MBa in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardThe temperature dependence of the vapor pressure is given by the equation: ΔΗ RT Inp = In A – Where: p= vapor pressure T = temperature A = pre-exponential constant AHvap = enthalpy of vaporization In order to solve for the enthalpy of vaporization, AHvap, you must: Step One Add the same expression to each side of the equation to leave the term that includes the variable by itself on the right-hand side of the expression: (Be sure that the answer field changes from light yellow to dark yellow before releasing your answer) ΔΗ RT + Inp = + In A Drag and drop your selection from the following list to complete the answer: 1 1 In In A - In A Karrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education