
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the given figure below, a 3.0 -kg block is sliding down a 60 degrees-rough incline. The speed of the block is 1.68 m/s at the instant it is 5.25 m from an uncompressed spring located at the other lower end of the incline. The spring has a spring or stiffness constant of 120 N/m and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is 0.35. (a) At what speed (in m/s) will the block strike the spring? (b) What would be the maximum compression (in m) of the spring?
8.6, 1.54
1.54, 8.6
8.2, 1.54
8.2, 1.45
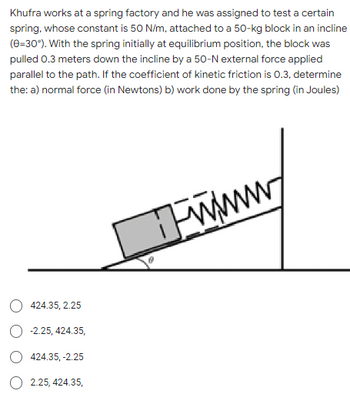
Transcribed Image Text:Khufra works at a spring factory and he was assigned to test a certain
spring, whose constant is 50 N/m, attached to a 50-kg block in an incline
(0=30°). With the spring initially at equilibrium position, the block was
pulled 0.3 meters down the incline by a 50-N external force applied
parallel to the path. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3, determine
the: a) normal force (in Newtons) b) work done by the spring (in Joules)
424.35, 2.25
-2.25, 424.35,
424.35, -2.25
2.25, 424.35,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When a 2.10-kg object is hung vertically on a certain light spring described by Hooke's law, the spring stretches 2.98 cm. (a) What is the force constant of the spring? (b) If the 2.10-kg object is removed, how far will the spring stretch if a 1.05-kg block is hung on it? (c) How much work must an external agent do to stretch the same spring 7.00 cm from its unstretched position?arrow_forwardThe system is released from rest with no slack in the cable and with the spring stretched 200 mm. Determine the distance s traveled by the 3.6-kg cart before it comes to rest (a) if m approaches zero and (b) if m = 2.4 kg. Assume no mechanical interference and no friction. The distance s is positive if up the incline, negative if down. k = 105 N/m 3.6 kg 25° m Answers: (a) m = 0, S = (b) m = 2.4 kg, S = iarrow_forwardA lab assistant has suspended a spring from a door frame. When an object is attached to the spring's bottom end, the spring extends downward by an additional distance, d, measuring 4.80 cm. (That downward distance is relative to the unstretched position that the spring had previously held when in equilibrium, as shown by the horizontal dashed line in the figure below). Calculate the mass of the hanging object (in kg) if the spring constant k has the value 59.5 N/m. 1. kgarrow_forward
- A 2.00 kg mass on a frictionless incline plane of angle 6 degrees is released and begins sliding down the incline. At the bottom of the incline is a spring (k=70 N/m). If the mass slides 0.30 m along the incline plane before it contacts the spring, how far is the spring compressed by the mass? (round to the nearest hundredth)arrow_forwardAn engineer is designing a spring to be placed at the bottom of an elevator shaft. If the elevator cable should break when the elevator is at a height of 103m above the top of the spring, calculate the value that the spring stiffness constant should have so that passengers undergo an acceleration of no more than 3.9g when brought to rest. Let 924kg be the total mass of the elevator and passengers.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON