
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
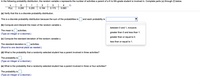
Transcribed Image Text:In this exercise, we examine a probability distribution where the random variable \( x \) represents the number of activities a parent of a K to 5th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (a) through (f) as instructed below:
| \( x \) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---------|------|------|------|------|------|
| P(x) | 0.295 | 0.255 | 0.194 | 0.173 | 0.083 |
**(a) Verify that this is a discrete probability distribution.**
- This is a discrete probability distribution because the sum of the probabilities is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_) and each probability is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
**Options for selection:**
- between 0 and 1, inclusive.
- greater than 0 and less than 1.
- greater than or equal to 0.
- less than or equal to 1.
**(b) Compute and interpret the mean of the random variable \( x \).**
- The mean is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) activities.
- *(Type an integer or a decimal.)*
**(c) Compute the standard deviation of the random variable \( x \).**
- The standard deviation is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\) activities.
- *(Round to one decimal place as needed.)*
**(d) What is the probability that a randomly selected student has a parent involved in three activities?**
- The probability is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
- *(Type an integer or a decimal.)*
**(e) What is the probability that a randomly selected student has a parent involved in three or four activities?**
- The probability is \(\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\).
- *(Type an integer or a decimal.)*
Follow the instructions to complete each step, ensuring calculations are accurate where necessary. This activity builds understanding of discrete probability distributions and their associated measurements.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the following probability distribution, the random variable x represents the number of activities a parent of a 6th- to 8th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (a) through (f) below. X 1 2 4 P(x) 0.321 0.345 0.156 0.063 0.115 (a) Verify that this is a discrete probability distribution. This is a discrete probability distribution because the sum of the probabilities is and each probability isarrow_forwardIn the following probability distribution, the random variable x represents the number of activities a parent of a 6th- to 8th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (aj 3 4 P(x) 0.314 0.261 0.204 0.083 0.138 (a) Verify that this is a discrete probability distribution. This is a discrete probability distribution because the sum of the probabilities is and each probability is less than or equal to 1. greater than 0 and less than 1. between 0 and 1, inclusive. greater than or equal to 0. Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. Clear All parts remaining MacBook Airarrow_forwardIn the following probability distribution, the random variable x represents the number of activities a parent of a K to 5th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (a) through (f) below. 1 2 3 4 P(x) 0.096 0.396 0.135 0.063 0.310 ..... (a) Verify that this is a discrete probability distribution. This is a discrete probability distribution because the sum of the probabilities is and each probability is between 0 and 1, inclusive. (b) Graph the discrete probability distribution. Choose the correct graph below. A. В. C. D. 0.5- 0.5- 0.5- 0.5- 0.4- 0.4 0.4- 0.4- 0.3- 0.3- 0.3 0.3- 0.2- 0.2- 0.2- 0.2- 0.1- 0.1- 01- 0.1- to to to 0- 0- 0- 0- 1 1 3 1 3 4 1 2 3 4 (c) Compute and interpret the mean of the random variable x. The mean is activities. (Type an integer or decimal. Do not round.) Which of the following interpretations of the mean is correct? A. The observed value of an experiment will be equal to the mean of the random variable in most experiments. B. As the number of…arrow_forward
- Let y denote the number of broken eggs in a randomly selected carton of one dozen eggs. Suppose that the probability distribution of y is as follows. y 0 1 2 3 4 p(y) 0.63 0.21 0.11 0.03 ? (a) Only y values of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 have positive probabilities. What is p(4)? (Hint: Consider the properties of a discrete probability distribution.) p(4) = (b) How would you interpret p(1) = 0.21? In the long run, the proportion that will have at most one broken egg will equal 0.21.In the long run, the proportion of cartons that have exactly one broken egg will equal 0.21. The probability of one randomly chosen carton having broken eggs in it is 0.21.The proportion of eggs that will be broken in each carton from this population is 0.21. (c) Calculate P(y ≤ 2), the probability that the carton contains at most two broken eggs. P(y ≤ 2) = Interpret this probability. The probability of two randomly chosen cartons having broken eggs in them is this probability.In the…arrow_forwardIn the following probability distribution, the random variable x represents the number of activities a parent of a K to 5th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (a) through (f) below.arrow_forwardIn the following probability distribution, the random variable x represents the number of activities a parent of a K to 5th-grade student is involved in. Complete parts (a) through () below. to 1 2 3 4 P(x) 0.299 0.084 0.131 0.213 0.273 (a) Verify that this is a discrete probability distribution. This is a discrete probability distribution because the sum of the probabilities is 1 and each probability is between 0 and 1, inclusive. (b) Graph the discrete probability distribution. Choose the correct graph below. YA. O B. OC. OD. 0.5- 04 Q 0.5- 0.5- 0.- 4- 0.4- 0.4- 0.4- 0.3- 0.3- 0.3- 0.3- 0.2+ 0.2- 0.2- 0.2- 0.1+ 0.1- 0.1- 0.1- 0- 0 1 0- 0 1 4 012 3 4 ó i 2 3 (c) Compute and interpret the mean of the random variable x. The mean is activities. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)arrow_forward
- The joint probability distribution function of X and Y is given by: 1 2 3 1 0.05 0.06 0.10 X 2 0.13 0.21 0.30 a. Find the conditional distribution of Y given X = 1 b. Find the conditional distribution of X given Y = 2 5 0.02 0.03 0.10arrow_forwardLet X = {Email, In Person, Instant Message, Text Message}; P(Email) = 0.06 P(In Person) = 0.55 P(Instant Message) = 0.24 P(Text Message) = 0.15 Is this model a probability distribution? A. Yes. B. No. C. Maybe.arrow_forwardAssume that 12 jurors are randomly selected from a population in which 75% of the people are Mexican-Americans. Refer to the probability distribution table below and find the indicated probabilities. xx P(x)P(x) 0 0+ 1 0+ 2 0+ 3 0.0004 4 0.0024 5 0.0115 6 0.0401 7 0.1032 8 0.1936 9 0.2581 10 0.2323 11 0.1267 12 0.0317 Find the probability of exactly 8 Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors.P(x=8)=P(x=8)= Find the probability of 8 or fewer Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors.P(x≤8)=P(x≤8)= IncorrectDoes the occurrence of 8 Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors suggest that the selection process discriminates against Mexican-Americans?arrow_forward
- Assume that 12 jurors are randomly selected from a population in which 80% of the people are Mexican-Americans. Refer to the probability distribution table below and find the indicated probabilities. xx P(x)P(x) 0 0+ 1 0+ 2 0+ 3 0.0001 4 0.0005 5 0.0033 6 0.0155 7 0.0532 8 0.1329 9 0.2362 10 0.2835 11 0.2062 12 0.0687 Find the probability of exactly 7 Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors. Round your answer to four decimal places.P(x=7)=P(x=7)= Find the probability of 7 or fewer Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors. Round your answer to four decimal places.P(x≤7)=P(x≤7)= Does 7 Mexican-Americans among 12 jurors suggest that the selection process discriminates against Mexican-Americans? no yesarrow_forwardLet y denote the number of broken eggs in a randomly selected carton of one dozen eggs. Suppose that the probability distribution of y is as follows. y 0 1 2 3 4 p(y) 0.63 0.19 0.11 0.05 ? (a) Only y values of 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 have positive probabilities. What is p(4)? (Hint: Consider the properties of a discrete probability distribution.) p(4) = Calculate P(y ≤ 2), the probability that the carton contains at most two broken eggs. P(y ≤ 2) = Calculate P(y < 2), the probability that the carton contains fewer than two broken eggs. P(y < 2) =arrow_forwardIn the probability distribution to the right, the random variable X represents the number of hits a baseball player obtained in a game over the course of a season. Complete parts (a) through (f) below. 10000 (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) X 0 1 2 3 4 5 P(x) 0.1666 0.3358 0.2857 0.1481 0.0383 0.0255 games. OD. Over the course of many games, one would expect the mean number of hits per game to be the mean of the random variable. (d) Compute the standard deviation of the random variable X. x = hits (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (e) What is the probability that in a randomly selected game, the player got 2 hits? ☐ (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) (f) What is the probability that in a randomly selected game, the player got more than 1 hit?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman