
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
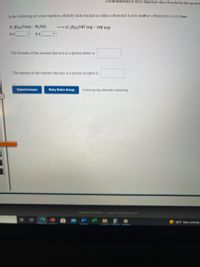
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to access important values if needed for this question
In the following net ionic equation, identify each reactant as either a Bronsted-Lowry acid or a Bronsted-Lowry base.
(C,H3)3N(aq) + H,0(1)
→ (C,H3)3NH*(aq) + OH(aq)
B-L
B-L
The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton donor is
The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton acceptor is
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
8 more group attempts remaining
Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Suppoet
98 F Rain coming
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- = O ACIDS AND BASES Identifying Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases For each chemical reaction in the table below, decide whether the highlighted reactant is a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Brønsted-Lowry base, or neither. reaction NH(aq) + OH (aq) → NH3(aq) + H₂O(1) NH3(aq) + H₂O(1)→ NH(aq) + OH(aq) NH4(aq) + OH (aq) ► NH3(aq) + H₂O(1) NH3(aq) + H₂O(1)→ NH(aq) + OH(aq) 1 highlighted reactant Bronsted-Lowry Bronsted-Lowry acid base O O O O O neither O O 0 0/5 Oarrow_forwardsearch ||| O ACIDS AND BASES Identifying Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases For each chemical reaction in the table below, decide whether the highlighted reactant is a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Brønsted-Lowry base, or neither. reaction I (aq) + H₂O (aq) HI(aq) + H₂O(l) HI(aq) + H,O) → I (aq) + H,O (aq) I (aq) + H,O (aq) → HI(aq) + H,O HI(aq) + H₂O(1) → I¯ (aq) + H₂O¯(aq) Ei Explmmation Check BROM C C S highlighted reactant Bronsted-Lowry Bronsted-Lowry neither acid base X $ 3/5 O Jessica V 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 000 Ar 图]arrow_forwardMatch the acid to the correct chemical equation showing its reaction with water. hydrochloric acid hypochlorous acid chlorous acid chloric acid perchloric acid A. HClO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO2−(aq) + H3O+(aq) B. HCl(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ Cl−(aq) + H3O+(aq) C. HClO2(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO2−(aq) + H3O+(aq) D. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq) E. HClO(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO−(aq) + H3O+(aq) F. HClO(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO−(aq) + H3O+(aq) G. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO4−(aq) + H3O+(aq) H. HClO3(aq) + H2O(l) → ClO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq) I. HClO4(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ ClO4−(aq) + H3O+(aq) J. HCl(aq) + H2O(l) → Cl−(aq) + H3O+(aq)arrow_forward
- In the following net ionic equation, identify each reactant as either a Bronsted-Lowry acid or a Bronsted-Lowry base. HClO(aq) + H2O(l) ClO-(aq) + H3O+(aq)B-L B-L The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton donor is The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton acceptor isarrow_forwardH2O(l) + H2O(l) <-> H3O^+(aq) + OH^-(aq) At 25degrees celsius, Kw = 1.00 x 10^-14 = [H3O^+][OH-] What is the concentration for hydroxide ion and hydronium ion?arrow_forwardAccording to LeChâtelier's principle, predict whether adding H₂O causes the system to shift in the direction of reactants, products, or no change. NH4+ (aq) + H₂O(1) ⇒ NH3(aq) + H3O+ (aq) reactants no change productsarrow_forward
- In the following net ionic equation, identify each reactant as either a Bronsted-Lowry acid or a Bronsted-Lowry base. C2H5NH2(aq) + H2O(l) C2H5NH3+(aq)(aq) + OH-(aq)B-L B-L The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton donor is The formula of the reactant that acts as a proton acceptor isarrow_forwardPredict the products of the following acid-base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow. HSO4−(aq)+CO3 2−(aq)⇌arrow_forwardThe OH⁻ concentration in an aqueous solution at 25 °C is 6.1 × 10⁻⁵. What is [H⁺]?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY