
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
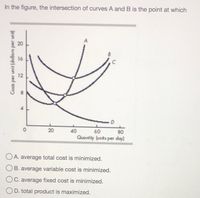
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure Explanation:**
The graph illustrates four different cost curves labeled A, B, C, and D. The x-axis represents "Quantity (units per day)," ranging from 0 to 80, and the y-axis represents "Cost per unit (dollars per unit)," ranging from 0 to 20.
- **Curve A**: Downward sloping, indicating decreasing costs with increased quantity and intersects with curve B at a certain point.
- **Curve B**: U-shaped, representing typical cost behavior as quantity increases, intersecting with curves A and C.
- **Curve C**: Appears to be upward sloping, increasing as quantity increases, overlapping slightly with curve B.
- **Curve D**: Downward sloping, below the other curves, suggesting decreasing costs with increased quantity.
The intersection of curves A and B indicates a critical point of cost analysis.
**Question:**
In the figure, the intersection of curves A and B is the point at which:
- A. average total cost is minimized.
- B. average variable cost is minimized.
- C. average fixed cost is minimized.
- D. total product is maximized.
This educational question prompts analysis of cost behaviors and optimization of production costs based on the interaction of these curves.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 15 3. Jane's Juice Bar has the following cost schedules: Quantity 0 vats of juice $0 1 10 12 25 3 45 4 70 100 135 10 1 12 13 14 15 Variable cost Total cost $30 40 55 75 100 130 165 Calculate average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost for each quantity. Put these numbers in the table below. Quantity Average variable cost Average total cost Marginal cost a. b. Graph all three curves (average variable cost, average total cost and marginal cost) using Excel or a piece of grid paper. Attach the graph to this assignment. What is the relationship between the marginal-cost curve and the average total cost curve? Between the marginal cost curve and the average variable cost curve? Explainarrow_forwardQuestion 6 Not yet answered Marked out of 1 Remove flag Drawinue nare If the average fixed cost of seven tubs of ice cream is $50, the total cost of zero tubs is: O a. $350 Ob. $250 c. $500 Od. $200 Clear my choice Next pagearrow_forwardQUESTION 6 At a total cost of $3,100, a company can produce 4 scooters. It has fixed costs of $1,000. If it produces 5 scooters, the costs of production total $3,800. Which of the following statements is true? O Variable costs of producing 4 scooters total $3096. O The average (or per unit) cost of producing 5 scooters is $800 per scooter The total cost curve for this firm is downward sloping Fixed costs will be higher when it produces 5 scooters The marginal cost of producing the fifth scooter is $700arrow_forward
- Output TC ($) 200 250 15 300 20 350 23 400 25 450 Refer to the information above to answer this question. If total variable cost decreases by 20% at all levels of output, what is ATC when output is 20? O a. $12 O b. $30 Oc. $10 O d. $16 O e. $80arrow_forwardRead the question and given information carefully. Show all necessary steps and reasoning that lead to the answers. You nead to draw graphs. a-Define diseconomies of scale and draw the long run average cost curve of a company that demonstrates diseconomies of scale b-List 2 reasons of diseconomies of scale and (in no more than 50 words for each reason) explain how each reason can contribute to diseconomies of scalearrow_forwardHelp answer point A. Building Constructionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education