
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
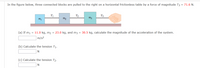
Transcribed Image Text:In the figure below, three connected blocks are pulled to the right on a horizontal frictionless table by a force of magnitude T3 = 71.6 N.
T2
T3
(a) If m1 = 11.0 kg, m2 = 23.0 kg, and m3 = 30.5 kg, calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the system.
m/s2
(b) Calculate the tension T1.
(c) Calculate the tension T2.
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the resultant ?R of the three tension forces acting on the eyt bolt. Find the magnitude of R and the angle θx which R makes with the positive x-axis. Note that F1= 563 N, F2= 345 N and F3= 296 N.arrow_forwardIn the following figure m_1 = 20.0 kg and angle = 51.4 degrees. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is μ_k = 0.40. a) What must be the mass (m_2) of the hanging block if it is to descend 13.5 m in the first 3.00 s after the system is released from rest?arrow_forwardThree boxes are pulled along a horizontal frictionless floor by a constant horizontal pull P. The boxes are connected by very light horizontal strings having tensions T1 and T2 as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements about the tensions is correct? T₂ T₁ 10 20 N N 100 N O A.T1 > T2 OB.T1 = P OC. T2 = P O D. T2 > T1 Parrow_forward
- A 2.00-kg object B is connected with a string to a 3.00-kgobject A, which is connected with a second string over a massless, frictionless pulley to a 8.00-kg object C. The strings have negligible mass and do not stretch, and the level tabletop is frictionless. Calculate the tension ?1. ?1= N Calculate the tension ?2. ?2= N Calculate the acceleration ? of the system. ?= m/s2arrow_forwardIn the system shown in figure m., m, and m2 are the masses of the bodies. The pulleys and threads have negligible masses and there is no friction. Find the acceleration of the body m,. Analyze the possible cases. mo m, m2 4m1m2+mo(m1-m2) g 4m,m2+mo(m1+m2) ansarrow_forwardTwo blocks with masses M1 and M2 hang one under the other. For this problem, take the positive direction to be upward, and use g for the magnitude of the free-fall acceleration. Assume accelerating the blocks are accelerating upward (due to the tension in the strings) with acceleration of magnitude a. a. Find T2, the tension in the lower rope. b. Find T1, the tension in the upper rope.arrow_forward
- In the figure below, three connected blocks are pulled to the right on a horizontal frictionless table by a force of magnitude T3 = 71.2 N. (a) If m1 = 12.5 kg, m2 = 23.5 kg, and m3 = 30.5 kg, calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the system. m/s2(b) Calculate the tension T1. N(c) Calculate the tension T2. Narrow_forwardCOMPLETE WITH FBD STEP BY STEP 2. A 15.0-kg load of bricks hangs from one end of an inextensible rope that passes over a small, frictionless pulley. A 28.0-kg counterweight is suspended from the other end of the rope. The system is released from rest. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the system? What is the tension acting on the rope? 28.0 kg 15.0 kgarrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected as shown. Their masses are m1 = 6.12 kg and m2 = 4.95 kg. The tabletop supporting Block 1 is frictionless. The masses for all strings and all pulleys in this problem are negligible. The friction in the pulleys is also negligible. Note the magnitude of the acceleration of mass m1 is twice that of mass m2 because of the way strings are connected to the two masses. 1. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration in m/s2 for Block 2? 2. Calculate the magnitude of the tension (in Newtons) in the string attached to Block 1?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON