Question
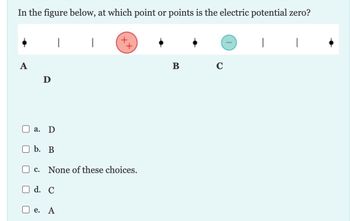
Transcribed Image Text:In the figure below, at which point or points is the electric potential zero?
A
D
a. D
b. B
I
d. C
C. None of these choices.
I
e. A
B
C
I
|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Define electric potential at a point:
VIEW Step 2: Find the expression for the potential due to the given charge configuration:
VIEW Step 3: Find the potential at point A:
VIEW Step 4: Find the potential at point B:
VIEW Step 5: Find the potential at point C:
VIEW Step 6: Find the potential at point D:
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2.arrow_forwardGiven this network, C2 T C1 4 uF 1uF 3 uF 03 A C4 2 uF C5 2 uF Assuming the dielectric of each capacitor is air and the network is connected to Vab = 30V supply, calculate the following: The equivalent capacitance between a and b. b. The charge of each capacitor. The potential difference on each capacitor d. Energy stored on each capacitor a. C. (Answers must be in Engineering Notation)arrow_forwardC2 C1 4 uF 1 uF C3 3 uF A- -B C4 2 uF C5 2 uf Assuming the dielecetrie of each capacitor is air and the network is connected to Vab = 30V supply, calculate the following: a. The equivalent capacitance between a and b. b. The charge on each capacitor. c. The potential difference on each capacitorarrow_forward
- A 30µF capacitor is charged to 80 V and then connected across an initially uncharged capacitor of unknown capacitance C. If the final potential difference across the 30µF capacitor is 10 V, determine C. Select one: a. 30 µF b. 90 µF C. 210 µF d. 20 µF e. 80 µFarrow_forward6 p6arrow_forwardTwo students were given a task to connect a 2 µF capacitor and a 6 µFcapacitor.A1. What type of connection will the 2 µF obtain a greater charge?a. series c. both a & bb. parallel d. neither a or bA2. What type of connection will the 2 µF obtain a greater potentialdifference?a. series c. both a & bb. parallel d. neither a or barrow_forward
- For items 4-5. Two students were given a task to connect a 2 µF capacitor and a 6 µF сaрacitor. 4. What type of connection will the 2 uF obtain a greater charge? c. both a & b a. series b. parallel 5. What type of connection will the 2 µF obtain a greater potential d. neither a or b difference? c. both a & b d. neither a or b a. series b. parallelarrow_forwardA. What is the potential difference (in volts) across C2 when C, = 5.0 pF, C2 = 15 µF, = 30 µF, and V% = 53 V? C3 Vo Select one: OA. 26.50 B. 17.67 OC. 79.50 D. 35.33 E. 48.76arrow_forwardI Review A 13.0 nC charge is at x = Ocm and a -1.4 nC charge is at = 3.0 cm Part A At what point or points on the a-axis is the electric potential zero? Express your answer in centimeters. If there is more than one answer, give each answer separated by a comma. Vα ΑΣφ ? x0 = cm Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- An electron is at rest near point 'A' and it is accelerated by an electric force toward point 'B'. This is because a. point 'A' is at a higher potential than point 'B'. b. point 'B' is at a higher potential than point 'A'. c. point 'A' and point 'B' are at the same potential. d. not enough informationarrow_forwardA series of equipotential lines are shown in the picture below. At what labeled location is the magnitude of the electric field the greatest? OV +10 V -10 V -20 V C. D. E. A В O Earrow_forwardA proton with an initial speed of 850,000 m/s is brought to rest by an electric field. ▾ Part A Did the proton move into a region of higher potential or lower potential? O Because the proton is a positive charge and it slows down as it travels, it must be moving from a region of higher potential to a region of lower potential. O Because the proton is a negative charge and it accelerates as it travels, it must be moving from a region of higher potential to a region of lower potential. O Because the proton is a negative charge and it accelerates as it travels, it must be moving from a region of lower potential to a region of higher potential. Because the proton is a positive charge and it slows down as it travels, it must be moving from a region of lower potential to a region of higher potential. Submit ✓ Correct Here we learn how to determine the distribution of the electric potential based on the movement of a charged particle. Part B Previous Answers What was the potential difference…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios