
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:In the diagrams, AD₁ and AS₁ are the "before" curves. Assuming Y₁ is full-employment output, an expansion is
depicted by
Multiple Choice
Opanel (A) only
panels (A) and (B)
panel (B) only.
panel (C) only
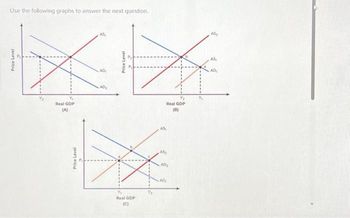
Transcribed Image Text:Use the following graphs to answer the next question.
Price Level
Real GDP
(A)
Price Level
AD₂
Price Level
X
Y₁
Real GDP
(C)
Real GDP
(8)
AS₂
AD₂
AD
AS₂
AS,
AD
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Changes in macroeconomic indicators can often be of relevance to business and influence decision-making concerning a range of issues related to things like profit forecasts, expected sales growth, expansion plans, etc. Assume you are employed as a business analyst with a large Singaporean based multinational corporation that manufactures electronic products. Identify and discuss how each of the following macroeconomic issues may be relevant to the firm. Rising unemployment in Singapore and other developed nations.arrow_forward14) The A) increase; rigid C) decline; flexible in employment during a recession is smaller if wages are B) decline; rigid D) increase; flexiblearrow_forwardSuppose country A has the following system of taxes/transfers: ANAL (a) Income 200: Taxed at 40%. In this country, we assume that everyone receives 5 per hour as wages. A worker chooses how many hours she wants to work. Her preferences over aggregate consumption, c, and 41 abor, I, are represented by the following utility function U(c, 1) =c+0ln(31-1) where 0 is a parameter reflecting drudgery of work (i.e. how painful the work is). Assuming 0 = 60 for the worker and given the system of axes/transfers, what is her optimal choice of labor? A 1=21 B 1 20 C 1* = 19 D 1*=22 48 55arrow_forward
- Lineararrow_forwardOur closed economy has a production function Y = A•F(K,LxE), where Y, K, L, E & A all have their usual meanings as per our lectures & course textbook. Also, this production function exhibits all the usual mathematical/economic properties we usually assume: positive marginal products, diminishing marginal products, complementarity between K & (LxE), and constant returns to scale. The aggregate consumption function depends negatively on the real interest rate, the government budget is balanced initially & the economy is in both a long-run equilibrium and steady state initially. The population growth rate is 2% per year, capital depreciates at a rate of 3% per year, the saving rate is 25% and technology is constant. Suppose the level of labour effectiveness (E) suddenly permanently rises by 10%. a) Use the long-run classical model to determine the qualitative impact of this shock on the long-run equilibrium levels of real output, consumption, investment, real interest…arrow_forwardConsider the following one-period model. Consumer Utility function over consumption (C) and leisure (L) U(C,L)= C^(1/2)L^(1/2) = Total hours: H = 40 Labour hours: = H – L Non-labour income: π Lump-sum tax: T Hourly wage: w Firm Production function: Y = zF() = z Total factor productivitiy: z = 2 Government Government spending (exogenous): G = 20 Suppose that the total factor productivity, z, increases to 5. What is the substitution effect of this wage change on labour supply()? A. +8.51 B. -5.51 C. -8.51 D. +5.51 E. None of the abovearrow_forward
- (1)The following macroeconomic model describes the economy of Sunderland. 1. Y= C +I + G + NX 2. C = 220 + 0.63 Y 3. 1 = 1000- 2000R 4. G = Go 5. NX = 525-0.10Y-50OR 6. M (0.1583Y-1000R)P (a)ls it a fair characterization to refer to equation #2 as a "simple" consumption function? Explain. (b)Derive the expression for equilibrium real output, Y, for this economy. Note: In your final expression for Y, restrict coefficient values to three decimal points. (c) Suppose government spending is 1200 , money supply by the Central Bank is 900 and the price level is 1, find the value of GDP (Y) and equilibrium interest rate (R) for Sunderland. Income Identity Consumption function Investment function Government Expenditure Net export function Money market equilibrium (2)The questions in this section are related to the macroeconomic model of Sunderland. (a)The expression you are asked to derive in question #1b can be considered an aggregate demand curve. Do you agree? Explain your answer. (b)Sketch…arrow_forwardConsider the following 2-period model U(C1,C2) = min{3C1,4C2} C1 + S = Y1 – T1 C2 = Y2 – T2 + (1+r)S Where C1 : first period consumption C2 : second period consumption S : first period saving Y1 = 20 : first period income T1 = 5 : first period lump-sum tax Y2 = 50 : second period income T2 = 10 : second period lump-sum tax r = 0.05 : real interest rate Find the optimal saving, S*arrow_forwardHello, I'm trying to figure out how this person got this answer. I get stuck at the line after the fourth equal sign. Could you please explain in detail how this was simplified? Thank you.arrow_forward
- do fast.arrow_forwardTyped plz and asap thanksarrow_forwardRefer to the figure below. Which of the points in the above graph are possible short-run equilibria? Price level (GDP deflator, 2000 = 100) O A and B O A and C O A and D O A, B, C, and D LRAS SRAS, SRAS₂ AD₂ AD₁ Real GDP (trillions of 2000 dollars)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education