
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
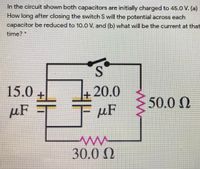
Transcribed Image Text:In the circuit shown both capacitors are initially charged to 45.0 V. (a)
How long after closing the switch S will the potential across each
capacitor be reduced to 10.0 V, and (b) what will be the current at that
time?
15.0
20.0
50.0 N
µF
µF
30.0 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A controller on an electronic arcade game consists of a variable resistor connected across the plates of a 0.220 mF capacitor. The capacitor is charged to 5.00 V, then discharged through the resistor. The time for the potential difference across the plates to decrease to 0.800 V is measured by a clock inside the game. If the range of discharge times that can be handled effectively is from 10.0 ms to 6.00 ms, what should be the (a) lower value and (b) higher value of the resistance range of the resistor?arrow_forwardA 1.5 V battery produces 44.6 mA when it is across a 30.0 0 load. The potential difference across the battery's terminals is_ V. Normal format with 3 SF.arrow_forward200T 80V 5. A 2.00 Farad capacitor, an 8.00 Q resistor and a 24.0 V battery are connected in series with a switch. The capacitor is initially uncharged. How long after the switch is closed (in seconds) does the charge on the capacitor reach one-fourth of its maximum value? (A) 3.50 (B) 4.60 (C) 2.98 (D) 7.21 (E) 6.43 (F) 10.5 2F 24Varrow_forward
- The capacitor in the figure has a capacitance of 35 µF and is initially uncharged. The battery provides a potential difference of 150 V. After switch S is closed, how much charge will pass through it?arrow_forwardE2 R1 R2 2. Find the charge on the capacitor after the switch has been left open for some time, then closed for some period of time. We can assume that C = 2 µF, with batteries of values E1 = 2V and E2 = 1 V, and resistor values R1 R2 = 0.25 2. 0.52 andarrow_forwardIn the circuit shown in Figure C₁ = 15.0μF, C₂ = 20.0μF, R₁ = 30.0Q2, R₂ = 50.0Q2. Both capacitors are initially charged to Vi = 45.0 V. a) Calculate the equivalent capacitance and the equivalent resistance. b) Calculate the charge accumulated on each capacitor. c) Calculate the time after closing the switch at which the potential across each capacitor will be reduced to V₁ = 10.0 V. S R₁ R₂ C₁- C₂ ‘TTarrow_forward
- 20V Hilt O O 20V 40V HI What is the potential difference for the 10 uF capacitor in the circuit shown? 12 12V 10 μF 15 µF 4 μFarrow_forwardFor the circuit shown in the figure, V = 20 V, C = 10 μF, R = 0.80 MQ, and the battery is ideal. Initially the switch S is open and the capacitor is uncharged. The switch is then closed at time t = 0.00 s. What is the charge across the capacitor 20 s after closing the switch? { www R O 0.18 mC O 1.5 mC O 0.48 mC O 3.0 MC O 2.3 MCarrow_forwardWhen an initially uncharged capacitor is charged through a 25-k resistor by a 75-V dc ideal power source, it takes 0.30 ms for the capacitor to reach 50% of its maximum charge? What is the capacitance of this capacitor?arrow_forward
- At what time t after the switch is closed is the voltage across the capacitor 8.00 V? Express your answer with the appropriate units. When the voltage across the capacitor is 8.00 V, at what rate is energy being stored in the capacitor? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forward2o2 3052 352 552 652 2A A. The power dissipated in the 3 Ohms resistor is W. B. The total voltage is V. C. The power dissipated in the 5 Ohms resistor is W. Round all answers to whole numbers.arrow_forward4. What value resistor will discharge a 1.0 µF capacitor to 10% of its initial charge in 2.0 ms?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON