
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
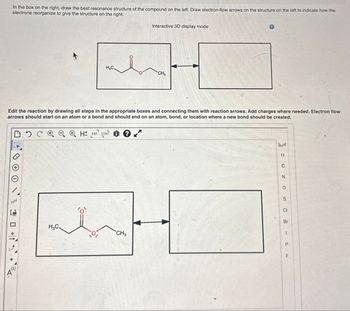
Transcribed Image Text:In the box on the right, draw the best resonance structure of the compound on the left. Draw electron-flow arrows on the structure on the left to indicate how the
electrons reorganize to give the structure on the right.
Interactive 3D display mode
CH₁₂
Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron flow
arrows should start on an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created.
H± EXP. CONT
を口か
H3C.
CH3
H
C
Zo S
CI
Br
P9
F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Draw the mechanism for the following reaction: H3C- CH3 P CH₂ -CH3 H₂C-OH H₂C CH3 CH3 CH3 -CH3arrow_forwardPlease see attachedarrow_forwardFor the given compound, draw all significant resonance forms and rank them from most significant to least significant. Briefly explain the rankings. Part 1 Let's begin by considering which resonance patterns are present. First, add curved arrow(s) to show the resonance using the following pattern: a pi bond between two atoms of differing electronegativity. Modify the second structure given to draw the new resonance structure. Include relevant formal charges in your structure. Use the + and - tools to add/remove charges to an atom, and use the single bond tool to add/remove double bonds. H₂C CH₂ H₂C Edit Drawing CH₂ SUPPORTarrow_forward
- The curved arrow notation introduced in Section 1.6B is a powerful method used by organic chemists to show the movement of electrons not only in resonance structures, but also in chemical reactions.Because each curved arrow shows the movement of two electrons, following the curved arrows illustrates what bonds are broken and formed in a reaction. Consider the following three-step process. (a) Add curved arrows in Step [1] to show the movement of electrons. (b) Use the curved arrows drawn in Step [2] to identify the structure of X. X is converted in Step [3] to phenol and HCl.arrow_forwardAnswer the given questionsarrow_forwardStep 3: Draw a curved arow to show formation of an oxygen-aluminum bond shown in the next panel. H C: + : 0: : 0: + + азаarrow_forward
- Please help, thank you so much for your time. Part A) Write a Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for OCSOCS and assign formal charges to each atom. Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons and formal charges. Part B Assign oxidation numbers to each of the atoms OO, CC, and SS in OCSOCS. Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. Part C Write a Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for SOCl2SOCl2 (SS is the central atom) and assign formal charges to each atom. Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons and formal charges. Part D Assign oxidation numbers to each of the atoms OO, SS, and ClCl in SOCl2SOCl2. Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Part E Write a Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for…arrow_forwardWhy was the formal charge of (+) placed on this carbon? I understand everything else about the question but can someone help me with explaining this. Thanks!arrow_forwardDraw all missing reactants and/or products in the appropriate boxes by placing atoms on the canvas and connecting them with bonds. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created.arrow_forward
- The curved arrow notation introduced in Section 1.6 is a powerful method used by organic chemists to show the movement of electrons not only in resonance structures, but also in chemical reactions. Since each curved arrow shows the movement of two electrons, following the curved arrows illustrates what bonds are broken and formed in a reaction. Consider the following three-step process. (a) Add curved arrows in Step [1] to show the movement of electrons. (b) Use the curved arrows drawn in Step [2] to identify the structure of X. X is converted in Step [3] to phenol and HCl.arrow_forwardThe curved arrow notation introduced in Section 1.6 is a powerful method used by organic chemists to show the movement of electrons not only in resonance structures, but also in chemical reactions. Since each curved arrow shows the movement of two electrons, following the curved arrows illustrates what bonds are broken and formed in a reaction. Consider the following three-step process. (a) Add curved arrows in Step [1] to show the movement of electrons. (b) Use the curved arrows drawn in Step [2] to identify the structure of X. X is converted in Step [3] to phenol and HCl.arrow_forwardDraw an arrow pushing pattern represents the flow of electrons that converts the first resonance structure into the second resonance structure?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning