
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
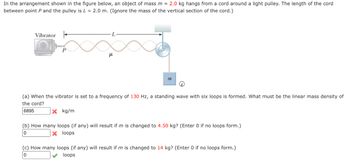
Transcribed Image Text:In the arrangement shown in the figure below, an object of mass m = 2.0 kg hangs from a cord around a light pulley. The length of the cord
between point P and the pulley is L= 2.0 m. (Ignore the mass of the vertical section of the cord.)
Vibrator
P
н
X kg/m
L
m
ii
(a) When the vibrator is set to a frequency of 130 Hz, a standing wave with six loops is formed. What must be the linear mass density of
the cord?
6895
(b) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed to 4.50 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.)
X loops
0
(c) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed to 14 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.)
0
loops
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the arrangement shown in the figure below, an object of mass m = 4.0 kg hangs from a cord around a light pulley. The length of the cord between point P and the pulley is L = 2.0 m. (Ignore the mass of the vertical section of the cord.) a Vibrator m (a) When the vibrator is set to a frequency of 170 Hz, a standing wave with six loops is formed. What must be the linear mass density of the cord? 3.05 10.31 kg/m (b) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed to 144 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.). 1 loops (c) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed to 10 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.) 4 Examine how changing the mass affects the wave speed and wavelength and how that affects the number of loops. loops Need Help? Read itarrow_forwardA standing wave pattern is created on a string with mass density p = 3 x 10-4 kg/m. A wave generator with frequency f = 62 Hz is attached to one end of the string and the other end goes over a pulley and is connected to a mass (ignore the weight of the string between the pulley and mass). The distance between the generator and pulley isL = 0.66 m. Initially the 2rd harmonic wave pattern is formed. 5)What is the wavelength of the wave? 6) What is the speed of the wave? 7) What is the tension in the string? 8) What is the mass hanging on the end of the string? 9) Keeping the frequency fixed at f = 62 Hz, what is the maximum mass that can be used to still create a coherent standing wave pattern?arrow_forwardA piano wire with mass 2.60g and length 81.0cm is stretched with a tension of 30.0N . A wave with frequency 110 Hz and amplitude 1.40 mm travels along the wire. (a)Calculate the average power carried by the wave. (b)What happens to the average power if the wave amplitude is halved?arrow_forward
- Mjc5NTA2NTk3NjEz (b) 0.8 sec; 14 m/s (c) 0.4 sec; 7 m/s (d)0.8 sec; 3.5 m/s 4) Two identical sinusoidal waves travel in the same direction at the same speed with an amplitude A. The phase difference between the two waves is o = 69.8°. The amplitude of the resultant wave, Aresultant» is increased with respect to the amplitude of the individual waves, A, by: (a) 18% (b) 64% (c) 82% (d) 164% 5) Two identical sinusoidal waves with frequency of 20 Hz travel in the same đirection at the same speen The two waves originate from the same point but with a time difference At. The amplitude of th AV3. The minimum possible time difference between the starting moments resultant wave is Ares the two waves is, At =: (a) 1/120 sec (b)0477 sec (c) 1/80 sec (d)0.716 sec rleueths of 2.5 m travel in the same direction with the Ih difference. Wave-1 traarrow_forwardIn the arrangement shown in the figure below, an object of mass m = 4.0 kg hangs from a cord around a light pulley. The length of the cord between point P and the pulley is L = 2.0 m. (Ignore the mass of the vertical section of the cord.) Vibrator- (a) When the vibrator is set to a frequency of 180 Hz, a standing wave with six loops is formed. What must be the linear mass density of the cord? kg/m (b) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed to 144 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.) loops (c) How many loops (if any) will result if m is changed 14 kg? (Enter 0 if no loops form.) loopsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON