Question
thumb_up100%
Explain the following solution to the problem

Transcribed Image Text:womos
Jn clarical mechawics
So the probakectity of
farticles is nglig ible and thus
heated as distingusishab le .
a cell untaining tuo r mane
ngligible
(oceu potime 1)
1 ) The pautily
camot be heated as diting wihable ,we theu une
when
vcu
Index
quantiur stati,ties.
at hower energies
FD
-3
- 2
MB
e
So BE and FD will an tend to Me.
when
Hightemperature and las
ぐ。
Condition.
when
TくY
strongly adogerarate
TくY
di «1
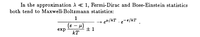
Transcribed Image Text:In the approximation A < 1, Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein statistics
both tend to Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics:
1
+ e4/kT . e-e/kT.
(€ — м)
exp
土1
kT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- L is a straight line in the plane, point A is at a distance of 2cm. from L Show how to draw a circle of radius length 3cm. such that it passes through A and its centre lies on the straight line L How many solutions can be carried out?arrow_forwardProblem 1:arrow_forwardPlease solve 34 and 35.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios