
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
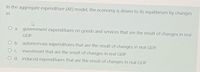
Transcribed Image Text:In the aggregate expenditure (AE) model, the economy is driven to its equilibrium by changes
in
a. government expenditures on goods and services that are the result of changes in real
GDP.
O b. autonomous expenditures that are the result of changes in real GDP.
investment that are the result of changes in real GDP.
O C.
O d. induced expenditures that are the result of changes in real GDP.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The aggregate expenditure method helps to understand the relationship between the economic activities of a country to its income level.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 47 An increase in the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) O a. increases the multiplier, so that changes in government spending have a larger effect on aggregate expenditure (aggregate demand). O b.increases the multiplier, so that changes in government spending have smaller effect on aggregate expenditure (aggregate demand). O c. decreases the multiplier, so that changes in government spending have a larger effect on aggregate expenditure (aggregate demand). O d. decreases the multiplier, so that changes in government spending have a smaller effect on aggregate expenditure (aggregate demand).arrow_forwardNo written by hand solutionarrow_forwardDuring 2019, a country reported that its real GDP increased by $3.0 billion. If the slope of its aggregate planned expenditure curve is 0.9, then which of the following might have led to the increase in real GDP? O a. Investment decreased by $0.3 billion. on O b. Exports increased by $0.3 billion. O c. Exports decreased by $0.3 billion. O d. Imports increased by $0.3 billion. O e. Government expenditure on goods and services increased by $3 billion.arrow_forward
- Quèstion 5 $60 $40 -- $20 $50 100 150 200 Disposable Income(Y) -20 Refer to the diagram. The average propensity to consume: O A. is greater than 1 at all levels of disposable income above $100. O B. cannot be determined from the information given. O C, is equal to the average propensity to save. O D. is greater than 1 at all levels of disposable income below $100. Saving (S)arrow_forwardIf taxes fall and government spending rises by the same amount, there is very little change in GDP. O True O Falsearrow_forward42arrow_forward
- 1. Aggregate expenditures and income The following table shows consumption (C), investment (1), government spending (G), and net exports (X-M) in a hypothetical economy for various levels of real GDP (Y). Assume that the price level remains unchanged at all levels of income. All figures are in billions of dollars. Compute aggregate expenditures for each income level and fill in the last column In the following table. Y с G 500 525 250 150 600 550 250 150 575 250 150 600 250 150 -200 900 625 250 150 -200 700 800 AL AGGREGATE EXPENDITURES (Billions of dollars) The following graph shows real GDP on the horizontal axis and aggregate expenditures (AE) on the vertical axis. The orange line (square symbols) represents a 45-degree (Y-AE) line. 1000 Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the aggregate expenditures line for this economy. Line segments will automatically connect the points. 900 300 I 700 X-M Aggregate Expenditures -200 725 -200 750 775 800 825 600 500 + -200 AE line *+…arrow_forwardImagine a 45°-line (Keynesian cross) diagram in which the upward-sloping aggregate expenditure curve intersects the 45°-line at point A. The economy is currently in macroeconomic equilibrium at output level Y.. Suppose that the price level increases. If the price level increases, the aggregate expenditures line will shift down The new equilibrium levels of GDP and expenditures will be O A. where the new AE line intersects the 45°-line. O B. unchanged. OC. anywhere on the new AE line ⒸD. where the new AE line interesects the original AE line.arrow_forwardAssume that MPS is 0.4. If spending increases by $8 billion, then real GDP will increase by Multiple Choice O O O O $15 billion. $20 billion. $13.3 billion. $8 billion.arrow_forward
- Moving to another question will save this response. Question 8 In an open mixed economy, the inflationary expenditure gap may be described as the O A. excess of GDP over Ca + lg +Xn +G at the full-employment output. O B. excess of Sa + M +T over lg +X+ G at the full-employment GDP. O C. excess of Ca + lg +Xn + G at the full-employment GDP. O D.extra consumption that occurs when investment increases in a full-employment economy. A Moving to another question will save this response.arrow_forwardQuèstion 1 In an open mixed economy, the inflationary expenditure gap may be described as the O A. excess of Sa + M+T over lg + X+ G at the full-employment GDP. O B. excess of GDP over Ca + lg +Xn + G at the full-employment output. OC excess of Ca + Ig + Xn + G at the full-employment GDP. O D. extra consumption that occurs when investment increases in a full-employment economy.arrow_forwardSuppose that the level of GDP increased by $100 billion in an economy where the marginal propensity to consume is 0.5. The initial change in spending must have been: O $5 billion O $100 billion O $50 billion O $500 billionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education