
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
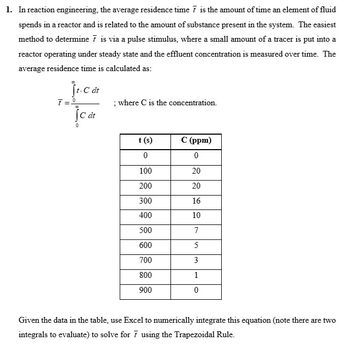
Transcribed Image Text:1. In reaction engineering, the average residence time 7 is the amount of time an element of fluid
spends in a reactor and is related to the amount of substance present in the system. The easiest
method to determine 7 is via a pulse stimulus, where a small amount of a tracer is put into a
reactor operating under steady state and the effluent concentration is measured over time. The
average residence time is calculated as:
Ĵt-C dt
7=º
JC dt
; where C is the concentration.
t (s)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
C (ppm)
0
20
20
16
10
7
5
3
1
0
Given the data in the table, use Excel to numerically integrate this equation (note there are two
integrals to evaluate) to solve for 7 using the Trapezoidal Rule.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A pasta company with a blue box produces 1,400 tons of semolina pasta per day. The pasta is fed into a machine as a large, loose dough and then squeezed through a bronze die to form a desired shape. As the pasta is squeezed through the die, the volume of space it takes up decreases while the mass remains constant, and thus the resulting shape is more dense. If m is the constant mass of the pasta in grams and V is the volume of the pasta in mL, then the density p is given by p= - m (a) If the mass remains constant while the volume changes with time, find dp dt (b) Suppose the mass of the pasta is 80g, the density is 0.8 g/mL, and the volume is decreasing at a rate of 400 mL/sec. How fast is the density of the pasta changing at that moment? mL · secarrow_forwardA student is concerned with the amount of air pollution students are exposed to in the school's parking lot after school. The student conducts an investigation to compare the quantity of particulate matter released from the diesel-powered buses, natural gas-powered buses, and the large and small cars as they idle waiting to pick up students. To make measurements, a small piece of white fabric is used to collect particulate matter from the tailpipe of each vehicle as it idles for five minutes. Each piece of fabric is then analyzed to measure the amount of particulate matter it collected. (i) Identify the independent variable in the investigation. (j) Identify one variable that was not mentioned in the description that could affect the results of the investigation. (k) Describe a realistic alternate sampling method to collect particulate matter from the vehicles in the investigation. (1) The student wants to ensure that the results are reliable. Explain how the student could modify the…arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

