
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
QUESTION FOUR
- In order to control traffic, a network router, A periodically sends a message to its neighbor, B, telling it to increase or decrease the number of packets that it can handle. At some point in time, Router A is flooded with traffic and sends B a message telling it to cease sending traffic. It does this by specifying that the number of bytes B may send (A’s window size) is 0. As traffic surges decrease, A sends a new message, telling B to restart transmission. It does this by increasing the window size from 0 to a positive number. That message is lost. As described, neither side will ever transmit. State and explain this type of deadlock.
- All precedence graph can be implemented by fork/join construct? Proof?
(i)Show by example that all precedence graphs cannot be implemented by cobegin/coend construct. Characterize the precedence graphs can be implemented using the cobegin/coend.
(ii)Explain how semaphore variables are used with cobegin/coend to be implemented in all precedence graphs.
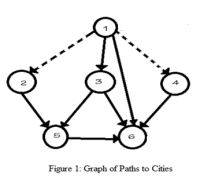
(iii)Apply the fork-join structure to write a procedure for the graph below in figure 1.
Apply the cobegin/coend with the aid of the semaphore variables to write a procedure for the graph below in figure 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Tower of Hanoi Problem Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical game consisting of three pegs (P1, P2 and P3) and a stack of disks of different diameters. Disks can slide onto any peg. The game starts with all disks stacked on P1 and ends at the point where all disks stacked on P3. The game player is required to move all disks from P1 to P3 using P2 as a buffer. Three rules must be followed when playing the game (1) Only one disk may be moved at a time. (2) Each move involves taking a disk on the top of a peg and place it on the top of another peg. (3) A disk of a larger diameter should never be placed on top of a disk of a smaller diameter. The diagrams below demonstrate the starting state and goal state of the game with 5 disks. starting sate p1 to goal state p3 Requirements In this assignment, students are required to solve the Tower of Hanoi (with five disks) using state space search algorithms implemented in Python. Two state space search algorithms: (1) a blind search (depth-first…arrow_forwardsee imagearrow_forwardExercise: A computer has 4 frames. Page size is 2KB (2048). The loaded time, the R and M bits for each page are shown below Page Frame Loaded time M R 11 1 15 3 13 4 5 5 7 6. 3 3 Question: compute the physical address of the following virtual address a) 1000 using FIFO b) 3100 using NRU c) 3100 using LRU d) 6200 using Second chance Note: consider each case separatelyarrow_forward
- Consider a disk queue with requests for I/O to blocks on cylinders 47, 38, 121, 191, 87, 11, 92, 10. The C-LOOK scheduling algorithm is used. The head is initially at cylinder number 63, moving towards larger cylinder numbers on its servicing pass. The cylinders are numbered from 0 to 199. The total head movement (in number of cylinders) incurred while servicing these requests isarrow_forwardConsider a computer environment in which there are 4 magnetic drives, 2 printers, 3 scanners, and 1 optical drive. Three processes P1, P2, P3 are using these resources. At any point in time, the allocations and requests for these resources are as follows. Allocations: Magnetic drive Printer Scanner Optical drive P1 1 P2 2 1 P3 1 Requests: Magnetic drive 2 Printer Scanner Optical drive P1 1 P2 1 1 P3 2 1 Is there any way that the processes can complete without deadlock? If yes, explain how. If not, explain why not.arrow_forward3. Consider the M/M/1 queue discussed in class. Assume that packets arrive to a queue with average arrival rate A [pkts/s]. The average service rate of the queue is denoted by u [pkts/s]. (a) Write expressions for: (i) the mean time between packet arrivals to the queue, i.e., the average inter-arrival time; and (ii) the mean service time, i.e., the average time needed to transmit a packet onto the outgoing link. (b) Let N denote the number of packets in the system in steady-state. Suppose A = 850 and u 1000. Find the smallest value of B such that P(N > B) < e = 10¬4. Hint: Use MATLAB or some other computational tool (you could even use an Excel spreadsheet) to test different values of B. 4. Consider the M/M/1 queue from Problem 3. (a) Find an expression for E[N], i.e., the average number of packets in the system in steady- state. For the values of A and µ specified in Problem 4(b), compute the value of E[N]. What happens when A→ µ? (b) Find an expression for Var[N], i.e., the variance…arrow_forward
- Consider a computer system with three users: Alice, Bob, and Cyndy. Alice owns the file alicerc, and Bob and Cyndy can read it. Cyndy can read and write the file bobrc, which Bob owns, but Alice can only read it. Only Cyndy can read and write the file cyndyrc, which she owns. Assume that the owner of each of these files can execute it. Create the corresponding access control matrix. Cyndy gives Alice permission to read cyndyrc, and Alice removes Bob's ability to read alicerc. Show the new access control matrixarrow_forwardQUESTION 5 The Towers of Hanoi game starts with a pile of disks with different sizes on one of three pegs. The other two pegs start empty. The disks are initially piled in order of size with largest on the bottom. The aim of the game is to transfer all of the disks to a destination peg by moving one disk at a time, never placing a disk on top of a smaller one. The spare peg may be used for intermediate moves. One solution to the problem recursively moves all but the largest disk to the spare peg, moves the largest disk to the destination peg, and then recursively moves all the other disks from the spare peg to the destination peg. This process is described by the following pseudocode: Hanoi( n, start, destination, spare ) // n is the number of disks and start, destination and spare are peg numbers if n>0 Hanoi( n-1, start, spare, destination) moveTopDisk( start, destination) // move top disk on start peg to destination peg Hanoi( n-1, spare, destination, start) Which of the following…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education