
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
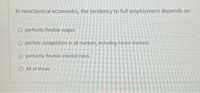
Transcribed Image Text:In neoclassical economics, the tendency to full employment depends on:
O perfectly flexible wages
O perfect competition in all markets, including factor markets
O perfectly flexible interest rates
O All of these
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
In neoclassical economics, if there is unemployment , it means that:
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
In neoclassical economics, if there is unemployment , it means that:
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that oil speculators buy oil and put it in storage. Shift one of the curves in the accompanying graph to show the effect of this speculation and then place the equilibrium point, E, at the new equilibrium price and quantity. What is the new price? $ Why is speculation advantageous for future consumption? O Speculation is not advantageous. Today's prices are higher than future prices. Future prices will be higher. O It tends to smooth prices over time. Price ($/barrel) 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 50 1 2 Is 4 D 3 4 5 6 Quanity (millions of barrerls) 7 8 9 10arrow_forwarda. Based on only the first-order condition with respect to labor computed in part a (Based on the given Lagrangian, compute the representative consumer's first-order conditions with respect to consumption and with respect to labor). Qualitatively sketch two things in a diagram with the real wage on the vertical axis and labor on the horizontal axis. First, the general shape of the relation ship between w and n (perfectly vertical, perfectly horizontal, upward-sloping, downward-sloping, or impossible to tell). Second, how changes in / affect the relationship (shift it outward, shift it in inward, or impossible to determine). Briefly describe the economics of how you obtained your conclusions. (Note: In this question you are not to use the first-order condition with respect to consump tion nor any other conditions.) b. Now based on both of the two first-order conditions computed in part a, construct the consumption-leisure optimality condition. Clearly present the important steps and…arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 In the neoclassical model, if the economy starts out on the LRAS (Long Run Aggregate Supply curve), with GDP equal to potential GDP, but then aggregate demand shifts to the left for any reason, what effect will this have in the long run? O a. Inflation O b. Higher real GDP Oc. Deflation and lower real GDP O d. Inflation and higher real GDP e. Deflation O f. Lower real GDParrow_forward
- In a life-cycle model, a worker with constant household productivity will react to an expected decrease in wages by Select one: O A. increasing his labor supply. O B. decreasing his labor supply. O C. not changing his labor supply, since the wage increase was expected. OD. either increasing or decreasing his labor supply.arrow_forwardSuppose our exports to Canada fall because of their recession. On impact, our will shift downward. Eventually, our will shift downward and the new equilibrium Tt will be O a. ADT; ASīt; higher O b. AST; ADt; higher AST; ADTt; lower O d. ADT; AST; lowerarrow_forwardEconomists use the neoclassical growth model to explain fluctuations in the business cycle because can; the model shows how economic growth changes when the factors of production (capital, labour force and technology) change. O cannot; the model does not take into account technology changes. O cannot; the model only explains what determines the long term trends in output or output per labour. O can; as a long-run model, it captures business cycles over very long periods of time. O cannot; the model is more focused on government activity than private sector activity. O Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education