
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:In longitudinal mechanical waves, rarefactions are the regions of .
a. high particle density, low air pressure
o b. high particle density, high air pressure
O C. low particle density, high air pressure
o d. low particle density, low air pressure
Approx
Light source
60°
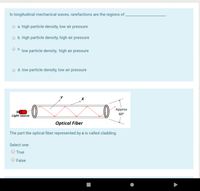
Optical Fiber
The part the optical fiber represented by x is called cladding.
Select one:
O True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- E6. Suppose that a guitar string has a length of 0.7 m, a mass of 0.14 kg, and a tension of 205 N. a. What is the mass per unit of length of this string? b. What is the speed of a wave on this string?arrow_forwardASK YOUR TEACHE DETAILS OBINPHYS8 6.P.009. ........................ ..... ************ l Verify the values given in the textbook for the wavelengths (in air) of the lowest and highest frequencies of sound that people can hear (20 and 20,000 Hz, respectively). (Round your answers to at least three significant figures in meters and assume air temperature to be 20°C.) lowest-frequency wavelength highest-frequency wavelength Submit Answerarrow_forwardParty hearing. As the number of people at a party increases, you must raise your voice for a listener to hear you against the background noise of the other partygoers. However, once you reach the level of yelling, the only way you can be heard is if you move closer to your listener, into the listener's "personal space." Model the situation by replacing you with an isotropic point source of fixed power Pand replacing your listener with a point that absorbs part of your sound waves. These points are initially separated by r = 1.10 m. If the background noise increases by Aß = 4.50 dB, the sound level at your listener must also increase. What separation rț is then required? Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- For the wave Y = 3cos(5t -6x), what are the following? a. Amplitude: b. Wavelength: c. Frequency:arrow_forwardQ5: Answer the following: a. Name the two characteristics of vibration analysis. b. Amplitude can be measured by three ways, list them. c. List four conditions that can be determined by vibration analysis. d. Explain the uses and application of x-ray. e. Explain the uses and application of thermo graphic testing.arrow_forwardOcean waves (on a particularly nice summer day) move past at1.5 waves/s. If the crest-to-crest distancebetween waves is4.0 m, then find the speed of the waves.4.A.5.618 m/sD.6.511 m/sB.4.817 m/sE.5.526 m/sC.6.000 m/sF.4.562 m/sarrow_forward
- The amplitude of two beating waves is described by the equation ψ = Amod(t)cos (ωavt). What is the main difference between this equation and the equation of a simple harmonic oscillator? A. The frequency changes in time. B. The amplitude changes in time. C. The phase changes in time.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true? Which one or more? a. The factors which affect speech intelligibility include noise, the available frequency range and peak clipping. b. Understanding speech requires signal to noise ratios greater than 12 dB. c. Transmission systems, such as telephone lines, generally pass the full range of speech frequencies. d. Continuous noise masks speech more than intermittent noise does.arrow_forward12. If 4 bugs make a sound of 14 dB then what will 25 bugs sound like? 13. Explain echoes. is the multi 14. Explain how band shells work. Ise words and a picture. qe obiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON