Question
thumb_up100%
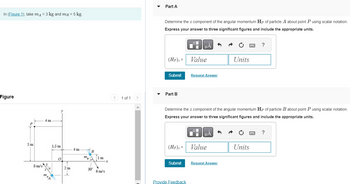
Transcribed Image Text:In (Figure 1), take m₁ = 3 kg and m³ = 5 kg.
Figure
5m
8 m/s
4m
3
1.5 m
O
0
2 m
4 m
mB
B
30°
1 m
6 m/s
x
< 1 of 1
Part A
Determine the z component of the angular momentum Hp of particle A about point P using scalar notation.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
(Hp)₂ =
Submit
Part B
μA
Submit
Value
Provide Feedback
Request Answer
Determine the z component of the angular momentum Hp of particle B about point P using scalar notation.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
(HP)₂= Value
HÅ
Units
Request Answer
wwwwww ?
Units
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please answer part (B) in the picture provided.arrow_forwardHELP WITH THIS PLEASE, DO NOT DO b ONLY THE OTHERarrow_forwardVector B→B→ has magnitude 7.30 and direction 14.0° below the +x-axis. Vector C→C→ has x-component Cx = −2.00 and y-component Cy = −6.70. a. What is the x-component of B→B→ ? b.What is the y-component of B→B→ ? c. What is the magnitude of C→C→ ? d. What angle does C→C→ make with the +x-axis in counterclockwise direction? A positive angle is counterclockwise from the +x-axis anwer in degrees e. What is the magnitude of C→+B→C→+B→ ? f. What angle does the resultant vector C→+B→C→+B→ make with the +x-axis in clockwise direction? A positive angle is counterclockwise from the +x-axis. asnwer in degrees g. What is the magnitude of C→−B→C→-B→ ? h. What angle does the vector C→−B→C→-B→ make with the +x-axis in counterclockwise direction? A positive angle is counterclockwise from the +x-axis. asnwer in degrees i. What is the x-component of C→−B→C→-B→ ? j.What is the y-component of C→−B→C→-B→ ?arrow_forward
- Case 1: A DJ starts up her phonograph player. The turntable accelerates uniformly from rest, and takes t1 = 11.6 seconds to get up to its full speed of f1 = 78 revolutions per minute. Case 2: The DJ then changes the speed of the turntable from f1 = 78 to f2 = 120 revolutions per minute. She notices that the turntable rotates exactly n2= 12 times while accelerating uniformly. a. Calculate the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the turntable (in radians/second2) while increasing to 120 RPM (Case 2). b. How long (in seconds) does it take for the turntable to go from f1 = 78 to f2 = 120 RPM?arrow_forwardFind the cross product →A × →C for (a) A = 2.0 ^i − 4.0 ^j + ^k and C = 3.0 ^i + 4.0 ^j + 10.0 ^k (b) A = 3.0 ^i + 4.0 ^j + 10.0 ^k and →C = 2.0 ^i − 4.0 ^j + ^k (c) A = −3.0 ^i − 4.0 ^j and →C = −3.0 ^i + 4.0 ^j (d ) →C = −2.0 ^i + 3.0 ^j + 2.0 ^k and A = −9.0 ^j Answer a and barrow_forwardVector B→B→ has magnitude 7.30 and direction 14.0° below the +x-axis. Vector C→C→ has x-component Cx = −2.00 and y-component Cy = −6.70. b. What is the y-component of B→B→ ? c. What is the magnitude of C→C→ ? d. What angle does C→C→ make with the +x-axis in counterclockwise direction? A positive angle is counterclockwise from the +x-axis. (answer in degreees) e. What is the magnitude of C→+B→C→+B→ ?arrow_forward
- Problem 1 Let A = 3 i - 3j +k and B= -2 i + (-1) j + 5 k. A. What is the cross product C = B x A ? B. What is the dot product C B?arrow_forward9c Qa О qb a/2 30 30 2 a/2 a R 90 a 90 a/2 a/2 6060 R R 30 r 30 30 90 90 30 a/2 a/2 a http://www.treenshop.com/Ireenshop/ArticlesPages/HiguresUninterest Article/The%20Equilateral%20 Triangle.htm qa = +1.8 nc, qb = -7.5 nC, qc = -8.7 nC, a = 30.0 cm The point charges are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side a. Determine the electric field at the center of the right side of the triangle. R || = r = 3 h 6 tarrow_forwardComputed mass of Pan X and Y (EV), and the percentage errorarrow_forward
- Consider the two vectors A= 12i + 5j and B = -3i. What is the cross product Ax B? O51 k none of the answers -15k O 15 j 15 k O.51 k -21 O 21 k -51arrow_forwardPlease see Part 4a.arrow_forwardThe member shown below is fixed at O and its dimensions are h1h1 = 1.10 mm, h2h2 = 0.20 mm, and ww = 0.50 mm. A force F of magnitude F=160N is applied at point C. Determine the magnitude of the moment of the force about point O.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios