
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
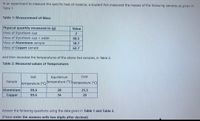
Transcribed Image Text:In an experiment to measure the specific heat of material, a student first measured the masses of the following samples as given in
Table 1.
Table 1: Measurement of Mass
Physical quantity measured in (g)
Mass of Styrofoam cup
Mass of Styrofoam cup + water
Mass of Aluminium sample
Mass of Copper sample
Value
60.5
18.7
62.7
and then recorded the temperatures of the above two samples, in Table 2.
Table 2: Measured values of Temperatures
Hot
Equilibrium
Cold
Sample
temperature (°C)
temperature ("C) temperature (°C)
Aluminium
99.6
28
25.5
Copper
99.6
34
28
Answer the following questions using the data given in Table 1 and Table 2.
(Please enter the answers with two digits after decimal)
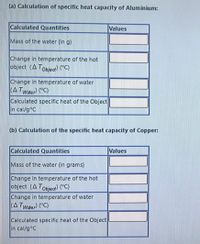
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Calculation of specific heat capacity of Aluminium:
Calculated Quantities
Values
Mass of the water (in g)
Change in temperature of the hot
object (ATobjed) PC)
Change in temperature of water
(A Twder "C)
Calculated specific heat of the Object
in cal/g°C
(b) Calculation of the specific heat capacity of Copper:
Calculated Quantities
Values
Mass of the water (in grams)
Change in temperature of the hot
object (A Tobjea) (°C)
Change in temperature of water
(A Twder "C)
Calculated specific heat of the Object
in cal/g°C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A calorimeter contains 100.0 g of water at 39.8 ºC. An 8.23 g metal object at 50.0 ºC is placed in the calorimeter. When equilibrium has been reached, the new temperature of the water and metal object is 40.0 ºC. What type of metal is the object made from (Refer to Table 1 )? (Assume that all the heat released by the metal was absorbed by the water.) Show all work with units. The answer must contain the correct units and the correct number of significant figures, pleasearrow_forwardCan some show me how to calculate the specific heat with the given information?arrow_forwardSUBJECT : GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 TOPIC : HEAT AND CALORIMETRYarrow_forward
- Can some show me how to calculate the specific heat with the given information?arrow_forwardA 45.90 g sample of pure copper is heated in a test tube to 99.40°C. The copper sample is then transferred to a calorimeter containing 61.04 g of deionized water. The water temperature in the calorimeter rises from 24.39°C to 29.10°C. The specific heat capacity of copper metal and water are J and 4.184 J 0.387 respectively. g. °C g. °C Assuming that heat was transferred from the copper to the water and the calorimeter, determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. Heat capacity of calorimeter-arrow_forward59.8 J was required to raise the temperature of 25.0 g of ethylene glycol by 1.00 K. Calculate the specific heat capacity of ethylene glycol. O a. 2.39 J/g.K O b. None of the above O c. 2.03 J/g.K O d. 1.39 J/g.K Next page Documents Jump to...arrow_forward
- SUBJECT : GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 TOPIC : HEAT AND CALORIMETRYarrow_forwardQ: A sample of gas expands from 40.0 L to 42.0 L at a constant pressure of 1 bar and receives 48 J of heat. Calculate ?U (in J) for the gas during this process. Answer in correct sig digsarrow_forwardWhen a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be determined using a coffee cup calorimeter. Thermometer Cardboard or In the laboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 0.46 g of MgCl,(s) are Styrofoam lid dissolved in 102.20 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 24.17 to 26.04 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.67 J/°C. Nested Styrofoam cups Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of MgCl2(s) in kJ/mol. Reaction occurs in Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water. solution. AHdissolution kJ/mol chookc Cngage Lngarrow_forward
- Mass of aluminum can 38.57 Mass of aluminum can and water 138.68 Mass of water 99.15 Initial mass of paraffin wax candle (before the experiment) 10.56 Final mass of paraffin wax candle (after the experiment) 10.45 Mass of paraffin wax consumed 0.16 Initial temperature of water and aluminum can calorimeter 23.3 Final temperature of water and aluminum can calorimeter 29.5 Change in temperature 0.4 Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion for paraffin wax.arrow_forwardThe “Miracle Thaw” is a device that defrosts frozen foods more quickly than when left out to the atmosphere. It is made of an aluminum alloy which has a (relatively) large specific heat. Explain why the engineers chose an alloy with a large specific heat for this task.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY