
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134217437
Author: Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
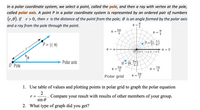
Transcribed Image Text:In a polar coordinate system, we select a point, called the **pole**, and then a ray with a vertex at the pole, called the **polar axis**. A point \( P \) in a polar coordinate system is represented by an ordered pair of numbers \( (r, \theta) \). If \( r > 0 \), then \( r \) is the distance of the point from the pole; \( \theta \) is an angle formed by the polar axis and a ray from the pole through the point.
### Diagram Explanation
- **Left Diagram**: Shows the basic representation of a polar coordinate system. The point \( P = (r, \theta) \) is located using the distance \( r \) from the pole \( O \) and angle \( \theta \) from the polar axis.
- **Right Diagram**: Depicts a polar grid with points plotted.
- The grid includes several concentric circles with radii marked (e.g., \( r = 1, 3, 5 \)).
- Various angles \( \theta \) (e.g., \( \theta = 0, \frac{\pi}{4}, \frac{\pi}{2}, \pi \)) are indicated along the circular grid.
- Specific points like \( P = (2, \frac{\pi}{4}) \) and \( Q = (4, \frac{5\pi}{4}) \) are highlighted on the grid, showing their positions relative to the pole.
### Exercises
1. Use a table of values and plot points on the polar grid to graph the polar equation \( r = \frac{2}{\sin \theta} \). Compare your result with results of other members of your group.
2. What type of graph did you get?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Convert the Cartesian coordinate (-2,-1) to polar coordinates, 0≤theta<2pi. round theta to nearest hundrethsarrow_forwardI. Convert the following coordinate systems (it is essential to show the procedure). 1. (2,-6) 2. (8,-2) 3. (10, 45°) 4. (4, π/2) Cartesian to polar or polar to Cartesianarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON
Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9780134217437
Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning