
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
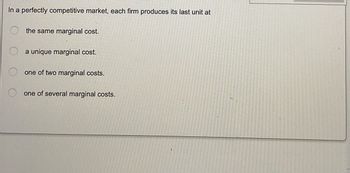
Transcribed Image Text:In a perfectly competitive market, each firm produces its last unit at
the same marginal cost.
a unique marginal cost.
one of two marginal costs.
one of several marginal costs.
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Equilibrium in Competitive Market in the Long Run The long-run average cost function of a competitive firm is AC(Q)= 40 − 6Q + Q2/3. The market demand curve is D(P) = 2200 − 100P. What is the long-run equilibrium price in this industry, and at thisprice, how much would an individual firm produce? How manyactive producers are in the market?arrow_forwarda) Describe the factors that drive profits to zero in perfectly competitive markets in the long run. Explain carefully the incentives that drive the market to a long run equilibrium. b) Why would a firm choose to operate at a loss in the short run? Explain carefully. c) When do firms decide to shut down production in the short run? Explain carefully.arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive firm is making a loss if price is greater than average total cost price is equal to average total cost price is less than average total cost marginal cost is equal to marginal revenuearrow_forward
- In a perfectly competitive market: marginal costs will be less than average costs. all firms will produce an equal amount of output. market price will equal the total cost of production. total industry costs of production are minimized.arrow_forwardUnder conditions of perfect or pure competition, or close to those conditions, producers (firms) are what are called “price takers”. This means that the price for the product that they are selling is determined by the market. No matter how little or how much product they supply, they can sell all they want at that price. If they were to price their product higher, they will sell zero. Which of the following is true? The price is equal to marginal revenue but not average revenue The price is equal to marginal revenue and average revenue The price is equal to average revenue but is not equal to marginal revenue The price is above both marginal revenue and average revenuearrow_forwardWhich of the following is true about a perfectly competitive firm in the long run and in the short run? The supply curve in the short run is usually steeper than the supply curve in the long run. The demand curve in the short run is usually steeper than the marginal cost curve in the long run. The supply curve in the short run is usually steeper than the average total cost curve in the long run. The supply curve in the short run is usually flatter than the supply curve in the long run.arrow_forward
- Assume that the market determined price is $10 in a perfectly competitive industry. A firm is currently producing 100 units of output. Average total cost is $8 while marginal cost is $8 and average variable cost is $6. Is the firm producing the profit-maximizing level of output? Why or why not? If not, what should the firm do?arrow_forwardIn the long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive market with identical firms, which of the following will be true? There will be no incentive for firms to enter or exit the market. Every firm will produce the quantity of output at which its average total costs are minimized. Every firm will earn 0 economic profit. All of the other choices will be true. Every firm's marginal cost will equal its marginal revenue.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education