
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I only need help with part b
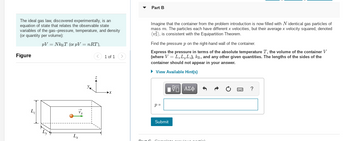
Transcribed Image Text:The ideal gas law, discovered experimentally, is an
equation of state that relates the observable state
variables of the gas--pressure, temperature, and density
(or quantity per volume):
PV = NkBT (or pV = nRT),
Figure
Lx
1 of 1
Part B
Imagine that the container from the problem introduction is now filled with N identical gas particles of
mass m. The particles each have different x velocities, but their average x velocity squared, denoted
(v²), is consistent with the Equipartition Theorem.
Find the pressure p on the right-hand wall of the container.
Express the pressure in terms of the absolute temperature T, the volume of the container V
(where V = L₂LyLz), kB, and any other given quantities. The lengths of the sides of the
container should not appear in your answer.
▸ View Available Hint(s)
p=
[Π ΑΣΦ
Submit
?
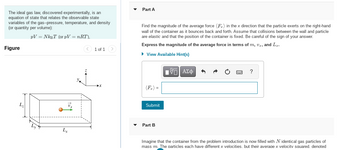
Transcribed Image Text:The ideal gas law, discovered experimentally, is an
equation of state that relates the observable state
variables of the gas--pressure, temperature, and density
(or quantity per volume):
PV = NkBT (or pV = nRT),
Figure
L₂
Lx
1 of 1
Part A
Find the magnitude of the average force (F) in the x direction that the particle exerts on the right-hand
wall of the container as it bounces back and forth. Assume that collisions between the wall and particle
are elastic and that the position of the container is fixed. Be careful of the sign of your answer.
Express the magnitude of the average force in terms of m, vr, and L₂.
► View Available Hint(s)
Submit
Part B
IVE ΑΣΦ
?
Imagine that the container from the problem introduction is now filled with N identical gas particles of
mass m. The particles each have different x velocities. but their average x velocity squared. denoted
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me with this worksheet on organic chemistryarrow_forwardMelting point started 54 and stopped 59 did you successfully make benzamide?arrow_forwardMCQ 4: Alkane molecules are not attacked by electrophiles or neutrophils because they are A. polar B. non-polar C. volatile D. unstablearrow_forward
- Hi please show your working out and make comments about what you are doing and why. This question also requires a detailed description of why you put the compounds from this question in that order.arrow_forward2. Draw out the following compounds. a. N-methylaniline b. Triisopropylamine c. N,N-dipropylhexylamine d. 1,5-pentanediamine (Also known as Cadaverine for its smell)arrow_forwardRank the following molecules in increasing order of water solubility and boiling point.arrow_forward
- Förčé Completion This test can be saved and resumed at any pc Remaining Time: 58 minutes, 20 seconds. Question Completion Status: A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 5 Draw at least 5 isomers for C5H11C1? Attach File Browse My Computer A Moving to another question will save this response.arrow_forwardPurpose of the boiling stones during the distillation process is: a. avoid the formation of bubbles b. prevent overheating of the solution c.help the liquid heat up faster d. help separate the components of the mixturearrow_forward1. Seliwanoff's test uses 6M HCl as dehydrating agent and resoncinol as condensation reagent. The test reagent dehydrates ketohexoses to produce a a. green compound b. violet precipitate c. faint pink color d. cherry red product 2. Bial’s test reacts with hexoses yield a a. red or pink product b. brown to grey product c. blue to purple color d. white precipitate 3. Bial’s test uses concentrated HCl as a dehydrating acid and orcinol + traces of ferric chloride as condensation reagent. The test reagent dehydrates pentoses to form furfural. Furfural further reacts with orcinol and the iron ion present in the test reagent to produce a a. bluish or green product b. red precipitate c. yellow solution d. light pink or pink solution 4. The copper sulfate (CuSO4) present in Benedict's solution reacts with electrons from the aldehyde or ketone group of certain sugars to form a carboxylic acid and a a. reddish…arrow_forward
- bad drove Use the following information to answer numerical-response question 9. Eight Common Compounds 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 C6H₂CH₂OOCCH3(1) Numerical Response 9. CO₂(g) C10H8(s) CaCO3(s) NaCIO(1) C3H6C1₂(1) NaHCO3(s) CH3COOH(aq) toodu The organic compounds above are numbered (Record all four digits of your answer in any order in the numerical-response section on the answer sheet.) andarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of increasing (lowest to highest) boiling point HO. II III -CH2-CH3 -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 II III HO. II IIIarrow_forwardMultiple Choice Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements is followed by answers or by completions of the statement. Select the one lettered answer or completion that is best in each case. Write your answer before each number. 48.A substance that has a high degree of purity and is used in direct standardization purposes: a. Analyzed reagent C. USP grade reagent b. Primary standard reagent d. Technical grade reagent 49. When a weak acid is titrated with strong base, the indicator used is a. Methyl red C. Titration not possible Methyl orange b. phenolphthalein d. 50.An organic compound that changes from one color to another at a certain pH is called: a. Indicator C. Standard solution b. Buffer d. Test solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY