Question
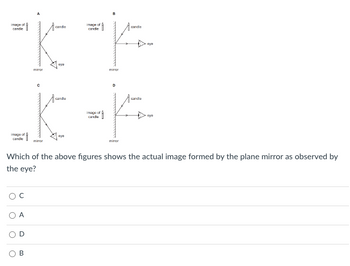
Transcribed Image Text:### Reflection in Plane Mirrors
**Question**
Which of the above figures shows the actual image formed by the plane mirror as observed by the eye?
**Diagrams and Explanations**
#### Diagram A
- **Description**: This diagram shows a candle in front of a plane mirror. The rays from the top and bottom of the candle pass through the mirror and converge at points where the observer (eye) would perceive the image. The image of the candle is located behind the mirror.
- **Key Points**: Image formation involves light paths reflecting off the mirror, converging to create an image behind the mirror.
#### Diagram B
- **Description**: This diagram displays a candle and a plane mirror. However, the light rays are not drawn correctly to indicate the actual position of the image as seen by the eye.
- **Key Points**: This representation does not show the image formation correctly.
#### Diagram C
- **Description**: Similar to Diagram A, this one also shows a candle in front of a plane mirror. The light rays travel towards the mirror and reflect back to the observer’s eye, indicating the perceived position of the image behind the mirror.
- **Key Points**: Correctly shows the formation of an image behind the mirror as perceived by the observer.
#### Diagram D
- **Description**: This diagram also shows a candle in front of a plane mirror, without the indication of light rays. The image position does not align with how the eye perceives the reflected beams.
- **Key Points**: Does not properly illustrate the image formation process.
**Options for Answer**
- \(\circ\) C
- \(\circ\) A
- \(\circ\) D
- \(\circ\) B
**Correct Answer:**
- The correct diagram is \(A\).
#### Explanation
Figure A correctly shows how the rays of light from the candle travel to the mirror and reflect back to the observer's eye, depicting the actual image formation behind the mirror.
Understanding the behavior of light in reflection off plane mirrors helps in visualizing how images are perceived, which is fundamental in optics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For a thin lens situaiton, you have detemined the image distance is negative. Which of the following must be true? the image is real, it is on the opposite side as the object the image is virtual, it is on the same side as the object the image is real, it is on the same side as the object the image is virtual, it is on the opposite side as the objectarrow_forwardA student attempts to determine the focal length of a mirror through graphical analysis. They make a series of observations by changing the position of an object and measuring the position of the corresponding focused image. When they graph their data to create a linear relationship, they obtain the following graph. (T-W) 'P/T 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 0.5 Observations of a Converging Mirror 1 1.5 2 1/d, (m¹) 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 Based on their graph, the best value for the focal length of the mirror, in meters, to two significant digits is:arrow_forwardThe figure below shows an object (in black) placed near a concave mirror. Possible images are shown with grey arrows, where solid arrows are real images and dashed arrows are virtual images. Which selection best represents the image formed by such an object? 2f B A F 00000arrow_forward
- convex spherical mirror with a radius of curvature of 16.5 cm produces a virtual image one half the size of the real object. Where is the object? cm (from the mirror)arrow_forwardA woman is 2 m tall, with her eyes at a height of 1.83 m. A mirror is on the wall, ending somewhat higher than her head. What is the highest point above the floor the bottom of the mirror can be so that she can still see her feet? You Answered 0.557 Correct Answer 0.915 margin of error- 1%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios