
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
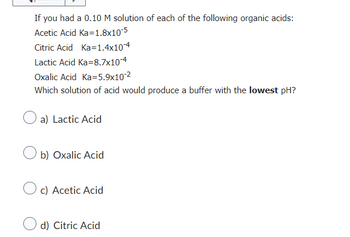
Transcribed Image Text:If you had a 0.10 M solution of each of the following organic acids:
Acetic Acid Ka=1.8x10-5
Citric Acid Ka=1.4x10-4
Lactic Acid Ka=8.7x10-4
Oxalic Acid Ka=5.9x10-²
Which solution of acid would produce a buffer with the lowest pH?
a) Lactic Acid
b) Oxalic Acid
c) Acetic Acid
d) Citric Acid
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you had a 0.10 M solution of each of the following organic acids: Acetic Acid Ka=1.8x10-5 Citric Acid Ka=1.4x10-4 Lactic Acid Ka=8.7x10-4 Oxalic Acid Ka=5.9x10-² Which solution of acid would produce a buffer with the highest pH? a) Acetic Acid b) Citric Acid c) Oxalic Acid d) Lactic Acidarrow_forwardIf you are going to prepare 100 ml each of the following two (2) buffers: • Buffer 1 will have a concentration of 0.2 M and a pH of 4.4 • Buffer 2 will have a concentration of 0.15 M and a pH of 8.9The buffering systems available to you are • dihydrogen phosphate/ hydrogen phosphate pKa= 6.8 • Tris-HCl/ Tris base pKa = 8.1 • acetic acid/ acetate pKa =4.8 What buffering system would you use for buffer 1 and buffer 2? why?arrow_forwardSubject: chemistryarrow_forward
- Which of the following combinations could not be used to make an effective buffer? O HNO2 and NaNO2 O NH,Cl and NH3 O CH,CO,H and NaCH,CO2 O NaHSO3 and NazSO4arrow_forwardWhich of the following solutions is a good buffer system? A solution that is 0.10 M HC2H3O2 and 0.10 M LiC2H3O2 A solution that is 0.10 M HF and 0.10 M NaC2H3O2 + A solution that is 0.10 M HCl and 0.10 M NH A solution that is 0.10 M NaOH and 0.10 M KOH None of the above are buffer systems.arrow_forwardDetermine the molar concentrations of Ca2+ and CI- in a 0.38 M calcium chloride solution. 1) 0.38 M Ca2+ and 0.38 M CI- O 2) 00.19 M Ca2+ and 0.38 M CI- 3) 0.38 M Ca2+ and 0.76 M CI- 4) 0.19 M Ca2+ and 0.76 M CI- O 5) None of the abovearrow_forward
- Which solution would be considered a buffer solution? 1) 0.50M NaF + 0.25M KF 2) 0.38M CH3COOH + 0.15M CH3COOH 3) 0.25M H2SO4 + 0.25M Na2SO4 4)1.25M LiNO3 + 0.50M HNO3 5) 0.50M NaCl + 0.50M HClarrow_forwardWhich of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? 0.10 M nitrous acid + 0.13 M sodium nitrite 0.31 M ammonium bromide + 0.31 M ammonia 0.29 M hydroiodic acid + 0.23 M potassium iodide 0.16 M potassium fluoride + 0.21 M hydrofluoric acid O 0.39 M acetic acid + 0.25 M potassium acetatearrow_forwardWhich of the following solutions is a buffer system?arrow_forward
- 19. A larger buffer capacity means that: more buffer is needed to neutralize a strong base the buffer is less resistant to changes in pH more buffer is needed to neutralize a strong acid the buffer is more resistant to changes in pHarrow_forwardWhich pair of compounds will form a buffer in aqueous solution? OHCN and HCl O NaCN and NaOH HCl and NaCl HCN and NaCN () NaCN and KCN HCl and NaOHarrow_forwardWhich of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems?(more than one answer maybe required) a) 0.40 M sodium bromide + 0.30 M calcium bromide b) 0.25 M ammonia + 0.31 M barium hydroxide c) 0.14 M hypochlorous acid + 0.17 M sodium hypochlorite d) 0.25 M hydrochloric acid + 0.23 M potassium chloride e) 0.14 M potassium hydroxide + 0.24 M potassium chloridearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY