
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
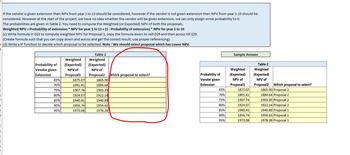
How do I write the formula to compute which proposal to select? The sample answer is given next to it. I need to write an “IF” statement and be able to drag that “IF” statement down to the other cells and for it to be correct.
Transcribed Image Text:7
If the vendor is given extension then NPV from year 1 to 13 should be considered, however if the vendor is not given extension then NPV from year 1-10 should be
considered. However at the start of the project, we have no idea whether the vendor will be given extension, we can only assign some probability to it.
The probabilities are given in Table 2. You need to compute the Weighted (or Expected) NPV of both the proposals.
Weighted NPV = Probability of extension * NPV for year 1 to 13+ (1 - Probability of extension) * NPV for year 1 to 10
(c) Write formula in D23 to compute weighted NPV for Proposal 1, copy the formula down to cell D29 and then across till E29.
(Create formula such that you can copy down and across and get the correct result, use proper referencing)
(d) Write a IF function to decide which proposal to be selected. Note: We should select proposal which has Lower NPV.
Probability of
Vendor given
Extension
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
Weighted
(Expected)
NPV of
Proposal1
1875.07
1891.41
1907.74
1924.07
1940.41
1956.74
1973.08
Table 2
Weighted
(Expected)
NPV of
Proposal2
1865.90
1884.64
1903.39
1922.14
1940.89
1959.63
1978.38
Which proposal to select?
Probability of
Vendor given
Extension
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
Sample Answer
Weighted
(Expected)
NPV of
Proposal1
1875.07
1891.41
1907.74
1924.07
1940.41
1956.74
1973.08
Table 2
Weighted
(Expected)
NPV of
Proposal2 Which proposal to select?
1865.90 Proposal 2
1884.64 Proposal 2
1903.39 Proposal 2
1922.14 Proposal 2
1940.89 Proposal 1
1959.63 Proposal 1
1978.38 Proposal 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Which of the following would be designed to estimate a numerical measurement of a population, such as monetary value?* A. Sampling for variables B. Sampling for attributes C. Sequential sampling D. Discovery sampling E. None of themarrow_forwardSuppose you're given a data set that classifies each sample unit into one of four categories: A, B, C, the data as A = 1, B=2, C = 3, and D=4. Are the data consisting of the classifications A, B, C, and D or quantitative? Are the data consisting of the classifications A, B, C, and D qualitiative or quantitative? OA. Qualitative, because they are measured on a naturally occuring numerical scale. B. Quantitative, because they are measured on a naturally occuring numerical scale. C. Quantitative, because they can only be classified into categories. D. Qualitative, because they can only be classified into categories. *** After the data are input as 1, 2, 3, or 4, are they qualitative or quantitative? OA. Qualitative, because they cannot be meaningfully added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided. B. Qualitative, because they are measured on a naturally occurring numerical scale. OC. Quantitative, because they are measured on a naturally occurring numerical scale. OD. Quantitative, because…arrow_forwardGive an example where researchers have used an event study and what did they find? Was it consistent with the EMH?arrow_forward
- What are the two major types of tests that have been performed totest the validity of the CAPM? (beta stability; slope of the SML)Explain their results.arrow_forwardb. Convert the Data available into a Table and choose a Design of your choice.c. Obtain the Mean, Median, Standard Deviation, Variance, Quartiles (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4), IQRfor the entire data (1895-1998), using ONLY Excel Functions (not using the Analysis ToolPak Add-In)d. Use the Statistical measurements generated from the Analysis Toolpak (Add-In) andcompare the values obtained in (c). Comment on your findings.arrow_forwardWhat is the criteria for judging the quality of research designs?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education