
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
If the track is designed so
that the passengers of
the roller coaster do not
experience a normal
force less than 1/2 or
more than 3 times their
weight, determine the
limiting heights hA and hC
so that this does not
occur. The roller coaster starts from rest at position A. Neglect friction.
Please show every single step of the process
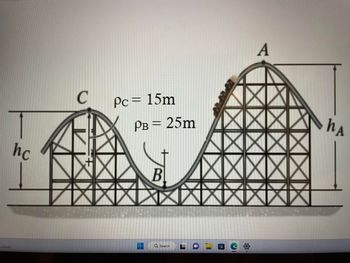
Transcribed Image Text:cloudy
hc
C
V
Pc = 15m
PB = 25m
8
B
Search
LO-
A
hA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cord is wrapped around the cylinder which is released from rest on the 60-degree incline. Find Vε(t) and Xε(t).arrow_forward6/20 The force P is applied to (a) the 60-lb block and (b) the 100-lb block. For each case, determine the magnitude of P required to initiate motion. H = 0.40- 60 lb P (a) 100 lb - H=0.12- Problem 6/20 P (b)arrow_forwardThe 20-lb block has friction coefficients of μ = 0.4 and = 0.35, with the inclined surface. Find a. the angle where the 10-lb block begins to slide b. the acceleration of the block at the angle where it first slides c. the acceleration of the block at an angle 10° past the angle in b. If you use cartesian coordinates with x-along the slope, the problem is easier. B Aarrow_forward
- Find the minimum force P required for impending motion of the block up the inclined surface, given: Mblock = 65 kg, θ = 52 °, μ = 0.4arrow_forwardThe smooth block B, having a mass of 1 kg, is attached to the vertex of the right circular cone using a light cord. If the block has a speed of 0.6 m/s around the cone, determine the tension in the cord and the reaction which the cone exerts on the block. Neglect the size of the block. 200 mm 400 mm 300 mmarrow_forwardThe robot arm is elevating and extending simultaneously. At a given instant, 0 = 34°,0 = 37 deg/s, 0 = 107 deg/s²,1 = 0.55 m, i = 0.37 m/s, and 7 = -0.36 m/s². Compute the radial and transverse forces F, and F that the arm must exert on the gripped part P, which has a mass of m = 20.8 kg. Compare with the case of static equilibrium in the same position. Assume d = 0.52 m. SASAARE Answers: Dynamic: Fr= Static: i i N, Fe= i N₁, Fe= i Z Z N Narrow_forward
- Q1: The 2-Mg truck achieves a speed of 15 m/s with a constant acceleration after it has traveled a distance of 100 m, starting from rest. Determine the normal force exerted on each pair of front wheels B and rear driving wheels A. Also, find the traction force on the pair of wheels at A. The front wheels are free to roll. Neglect the mass of the wheels Ans.: NB = 10729.3 N, NA = 8890.71 N traction force FA = 2250 N 0.75 m 2 m 1.5 m- $3 Barrow_forwardC14-2. As the large ring rotates, the operator can apply a breaking mechanism that binds the cars to the ring, which then allows the cars to rotate with the ring. Assuming the passengers are not belted into the cars, determine the smallest speed of the ring (cars) so that no passenger will fall out. When should the operator release the brake so that the cars can achieve their greatest speed as they slide freely on the ring? Estimate the greatest normal force of the seat on a passenger when this speed is reached. Use numerical values to explain your answer.arrow_forwardDetermine the steady-state angle a if the constant force P = 170 N is applied to the cart of mass M = 43 kg. The cart travels on the slope of angle 0 = 17°. The pendulum bob has mass m = 9 kg and the rigid bar of length L = 1.1 m has negligible mass. Ignore all friction. M L m Answer: a = iarrow_forward
- I have already done the question, but have some questions on the steps, please just answer that. The solution is already provided. Please answer with depth and clarity. A 200-kg crate is placed on a platform and moved vertically through a hydraulic cylinder BE that exerts a vertical force of F=1.5 kN. Determine the force developed in links AB and CD at the instant θ=90°. The platform is at rest when θ=45°. Neglect the mass of the links and the platform.arrow_forwardA 480-lb lawn roller is to be pulled over a curb with a height of 8 in. as shown. Determine the minimum pulling force that must be applied by the man to just start the 4-ft diameter roller over the curb. Also determine the angle θ which gives the minimum pulling force. Assume that the pulling force is along the handle, which makes an angle of θ with the horizontalarrow_forwardDetermine the steady-state angle α if the constant force P = 180 N is applied to the cart of mass M = 9 kg. The cart travels on the slope of angle θ = 16°. The pendulum bob has mass m = 3 kg and the rigid bar of length L = 1.2 m has negligible mass. Ignore all friction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY