
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
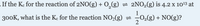
Transcribed Image Text:-If the Ke for the reaction of 2NO(g) + O,(g) = 2NO2(g) is 4.2 x 1013 at
300K, what is the Ke for the reaction NO2(g) =
O2(g) + NO(g)?
2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a particular reaction at 298 К., Кр 3.445 x 10^-3. When the same reaction is re-run at a lower temperature (155 K), Kp = 1.690 x 10^-5. The reaction is ................ a)endothermic exothermic atequilibrium complete .arrow_forwardThe Kp for the reaction A (g)=2 B (g) is 0.0830. What is Kp for the reaction 2 A (g)=4 B (g)?arrow_forwardAt 292.8 oC, the Kp for the reaction is 4.23⋅10-5: 3A+5B ↔ 1ABWhat is Keq?arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction CO₂ (g) +CCL, (g) -2000L₂ (g) 2COCL Calculate A-G for this reaction at 125 °C under the following conditions Pco, 0.105 bar 0.175 bar Poc, Pcoci,-0.735 bar A.G= 55.28 ΑΣΦ H C Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again: One attempt remaining ? kJ molarrow_forwardThe following reaction has a Keq = 195 at 1000 K. + CH4 (g) CO (g) + 3H2(g) → H₂O(g) If a vessel is filled with these gases such that the initial concentrations are [CO] = 0.036 M, [H₂] = 0.045 M, [H₂O] = 0.020 M, and [CH4] = 0.032 M, in which direction will a reaction occur and why? Towards products because Q = 0.38. Towards reactants because Q = 0.24. Towards products because Q = 4.1. Towards products because Q = 61. Neither direction; it is at equilibrium.arrow_forward14.98 The equilibrium constant Kc for the synthesis of methanol (i.e. CH3OH) with reaction CO(g) + 2H2(g) CH3OH8) is 4.3 at 250 °C and 1.8 at 275 °C. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic?arrow_forward
- Nitrogen tetroxide dissociates as follows: N2O4 → 2NO2 If a 100ml flask contains 1.00gm of N2O4 that is 30% dissociated at 40 C, what is the pressure inside the flask in atmospheres?arrow_forwardGiven the following equilibrium constants at 700K, 2 N2O(g) (double arrow) 2 N2 (g) + O2(g) K1 = 8.2 x 1033NO2(g) (double arrow) 1⁄2 N2(g) + O2(g) K2 = 2.44 x 108N2O4(g) (double arrow) 2 NO2(g) K3 = 4.6 x 10-3 determine the values of the equilibrium constants for the following reaction. Show your equation-buildingprocess and your calculations. 2 N2O4(g) (double arrow) 2 N2O(g) + 3 O2(g) K =arrow_forwardThe value of KC for the thermal decomposition of hydrogen sulfide, shown below, is 2.2 × 10-4 at 1400 K.2H2S(g)<--->2H2(g)+S2(g) A sample of gas in which [H2S] = 3.85 M is heated to 1400 K in a sealed vessel. After chemical equilibrium has been achieved, what is the value of [H2S]? Assume no H2 or S2 was present in the original sample.arrow_forward
- Consider the equilibrium system described by the chemical reactionbelow. Calculate the value of Qc for the initial set reaction conditions in3.00 L container:8.65 g C2H4, 11.2 g O2, and 5.68 g CH3CHO. 2 C2H4(g) + O2(g) = 2 CH3CHO(g)arrow_forwardConsider the quilibrium reaction between X and Y, as shown below: X=Y AG The reaction is started with 10 mmol of X; no Y is initially present. After 48 hours, analysis reveals the presence of 10 mmol of X and 0 mmol of Y. Which is the most likely explanation? = −1 - 45 kJ mol X and Y have reached equilibrium concentrations. An enzyme has shifted the equilibrium toward X. Formation of Y is kinetically slow; equilibrium has not been reached by 48 hours. Formation of Y is thermodynamically unfavorable. Two of the above explanations are reasonable.arrow_forwardFor which one of the following reactions is Kp equal to Kc? CaCO3(s) = CaO(s) + CO₂(g) 2NH3(g) = 3H₂(g) + N₂(g) 302(g) = 203(g) SnO2(s) + 2H₂(g) Sn(s) + 2H₂O(g) NH41(s) NH3(g) + HI(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY