
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
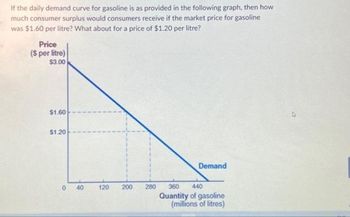
Transcribed Image Text:If the daily demand curve for gasoline is as provided in the following graph, then how
much consumer surplus would consumers receive if the market price for gasoline
was $1.60 per litre? What about for a price of $1.20 per litre?
Price
($ per litre)
$3.00
$1.60
$1.20
040
120
200
280
Demand
360 440
Quantity of gasoline
(millions of litres)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the Canadian demand for and the Japanese supply of cars to Canada is shown in the table below (quantities in thousands). Quantity Supplied (before tariff) Quantity supplied (after tariff) Price ($) 13,000 14,000 15,000 16,000 17,000 18,000 19,000 20,000 Quantity Demanded 170 150 130 110 90 70 50 30 50 70 90 110 130 150 170 190 a) The present equilibrium price is $ and quantity is b) Suppose that the Canadian government imposes a $2,000 per car tariff on imported Japanese cars. Show the new supply in the last column above. thousand. thousand. c) The new equilibrium price is $ and quantity is d) The total revenue received by the government will be $ e) Assume, instead, that the government imposes an import quota of 90,000 cars. The new equilibrium price is $ quantity is thousand. f) Does the government now receive any revenue? No million. andarrow_forwardConsider a hypothetical market for copper (q), where q is measured in 1000 tons. Suppose the supply of virgin copper is Sv = 10+5q. Suppose that the supply for recycled copper is Sr = 15+2.5q. Demand for copper is P = 65 - 1.5q. Note, buyers don't distinguish between recycled and virgin copper. The equilibrium price and output for copper is (hint: draw a graph) q=8.46, p = $52.31. q=0, p = $65. q=12.50, p = $46.25. O q=4.44, p = $58.33.arrow_forwardIn the market for hand sanitizers the demand function is given by: q = 80 - p, where q is the quantity of hand sanitizers (in thousands) and p is the price of hand sanitizers in dollars. Suppose the current market price for hand sanitizers is $4. 1. What is the inverse demand function equal to? Draw it in a diagram. 2. At a price of $4, what is the level of consumer surplus? 3. Due to the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic, people's preferences for sanitizing their hands change in favor of hand sanitizers. In fact, for any given price of hand sanitizers, people now want to purchase 20 units (in thousands) more hand sanitizers. o What is the new demand curve? o What is the new inverse demand curve? o Draw the new inverse demand curve in your diagram. 4. Suppose that after the increase in demand, the new price becomes $8. What is consumer surplus equal to at this new price (and with the new inverse demand curve)? 5. [Challenge Question] What would the consumer surplus be if the government…arrow_forward
- What is the consumer surplus in the market equilibrium? Again, the equations are: Qs = 3P-90 Qd = 400 - 5Parrow_forwardS₁ S₂ XX D Quantity (per period) Panel A Panel C D₂ D₁ Quantity (per period) panel A panel B panel C panel D Panel B S₂ D Quantity (per period) Panel D S₁ S D₁ D₂ Quantity (per period) The figure shows how supply and demand for rental cars during the Thanksgiving holiday might shift in response to specific events. Suppose a late season hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico destroys gasoline refineries in Louisiana. Which panel best describes how this will affect the market for rental cars?arrow_forwardAbove is the demand schedule for tickets to a Carnegie Hall performance of the Grateful Dead. Carnegie Hall seats 1,800 people. What is the equilibrium price and quantity for a concert of the Grateful Dead at Carnegie Hall? If tickets were sold for $18, what would happen (be specific)?arrow_forward
- Each rectangle on the graph corresponds to a particular seller in this market: blue (circe symbols) for Andrew, green (triangle symbols) for Beth, purple (diamond symbols) for Darnell, tan (dash symbols) for Eleanor, and orange (square symbols) for Jacques. (Note: The name labels are to the right of the corresponding segment on the supply curve.) Use the rectangles to shade the areas representing producer surplus for each person who is willing to sell a motor scooter at a market price of $70. (Note: If a person will not sell a motor scooter at the market price, indicate this by leaving their rectangle in its original position on the palette.) ? PRICE (Dollars per motor scooter) 160 140 120 100 180 60 40 20 0 0 Andrew 2 K Bet Darnell Jacques Eleanor 5 3 QUANTITY (Motor scooters) Market Price 6 7 8 ITI Andrew Beth Damell Eleanor 8 8 Jacquesarrow_forward2. For a particular commodity, the supply and demands functions are given by S(q) = 2q, D(q) = √192-8q where q is thousands of units and p is the the price per unit in dollars. (a) What is the equilibrium quantity q* and price p*? (b) Calculate the consumer's surplus and interpret your result.arrow_forwardMoney demand is likely to increase the most during which part of the business cycle? A. peak B. recession C. contraction D. trough E. recoveryarrow_forward
- 14. Over the past few year’s consumer tastes and the number of buyers in the market for a game called ‘pickle ball’ have increased dramatically. Thus, the demand for tickets to pickle ball events has increased. Before this all started the equilibrium price of a ticket to a pickle ball event was negative. This means that: A few years ago, there would have been a surplus of tickets even at a price of zero, now the invisible hand has pushed prices to greater than zero. A few years ago, the quantity of tickets demanded was less than quantity supplied. Pickle ball event tickets resembled the market for recyclable cardboard a few years ago Greater demand for pickle ball tournament tickets will lead to a greater demand – and higher pay – for professional pickle ball players. All of the above. B and D onlyarrow_forwardConsider that the retail market for sanitizing wipes in a small locale is described by the follow demand and supply equations respectively: P = 8.40 - 0.02Q and P = 6.60 + 0.01Q where P is the price in dollars and Q is the quantity measured in thousands per week. The market is currently in equilibrium. (Question 8 of 8) Now consider than an unexpected viral outbreak led to consumers ensuring that much more surfaces (counter tops, door handles, etc.) are clean and sanitized. At the same time, the government's demand for sanitizing wipes at various public institutions (hospitals, schools, etc.) has impacted the supply of sanitizing wipes in the retail market. Although the government is neither a buyer nor seller in the retail market, their requests for sanitizing wipes does affect how many sanitizing wipes firms are able to supply in the retail market. The market for sanitizing wipes adjusts afterwards and the market is in equilibrium. Suppose that after the market for sanitizing wipes…arrow_forwardpart Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education