
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
If the cord at B suddenly fails, determine
a) The angular acceleration of the beam.
b) The horizontal and vertical components of the initial reaction at pin A.
The beam has a mass of 50 kg. Treat the beam as a uniform slender rod.
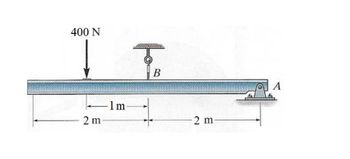
Transcribed Image Text:400 N
2m
-1m
कृ
B
-2m
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please show stepsarrow_forwardA torque T = 0.30 N-m is applied to a bevel gear B. Bevel gear D meshes with gear B and drives pump A. Gear B has a radius of gyration of 150 mm and a weight of 50 N, whereas gear D and the im- peller of pump A have a combined radius of gy- ration of 50 mm and a weight of 100 N. Find how many revolutions of gear B are needed to get the pump up to 200 rpm from rest. What is the power output of the pump at this speed if it is 90% efficient.arrow_forward2. A homogeneous cube, each edge of which has a length I, is initially in a position of unstable equilibrium with one edge in contact with a horizontal plane. The cube is then given a small displacement and allowed to fall. Show that the angular velocity of the cube when one face strikes the plane is given by w² = A (J2-1) where A=3/2 if the edge can not slide on the plane and where A=12/5 if sliding can occur without friction.arrow_forward
- SAMPLE PROBLEM 6/2 The vertical bar AB has a mass of 150 kg with center of mass G midway be- tween the ends. The bar is elevated from rest at 0 = 0 by means of the parallel links of negligible mass, with a constant couple M = 5 kN•m applied to the lower link at C. Determine the angular acceleration a of the links as a function of 6 0.6 m B 1.5 m and find the force B in the link DB at the instant when 0= 30°. 1.8 m Solution. The motion of the bar is seen to be curvilinear translation since the bar itself does not rotate during the motion. With the circular motion of the mass center G, we choose n- and t-coordinates as the most convenient descrip- LO 1.5 m A Marrow_forwardThe 136-kg spool has a radius of gyration about its mass center of kg = 300 mm. If the couple moment is applied to the spool and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the spool and the ground is u = 0.2, determine the angular acceleration of the spool, the acceleration of G and the tension in the cable. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the angular acceleration of the spool. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA a = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Figure < 1 of 1 Determine the acceleration of G. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0.4 m В HÀ ? 0.6 m Value Units aG = M = 450 N-m Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardThe 3.0 kg pendulum with mass center G is pivoted at A to the ficed support CA. It has a radius of gyration of 425 mm about O-0 and swings through an amplitude 0 pendulum is in the extreme position, calculate the moments Mx, M, and M, applied by the base support to the column at C. (M, = -5.64NM, M, = 1.976NM) 60°. For the instant when the 200 mm 400 mm 500 mmarrow_forward
- 2. The uniform bar of mass 5-kg and a length of 0.5 m is balanced in the vertical position when a horizontal force of P = 20 N is applied to the roller at A. Determine the bar's initial angular acceleration and the acceleration of its top point B. Barrow_forwardThe 250-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its center O of ko = 260 mm, and radius r = 0.4 m. When the wheel is subjected to the constant couple moment M = 64 N.m, it starts rolling from rest. Determine the total angular impulse L (in N.m.s) about the wheel's IC after 7.3 seconds if the wheel has been rolling without slipping. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². M Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardIn the figure below, the ring E has a mass mẸ = 30 kg and a radius of gyration about its center C of kc = 250 mm. A load mp = 40 kg carried by the ring E has an initial downward velocity 1.2 m/s when a clockwise torque is applied to the drum A to maintain a constant force F = 480 N in the cable at B. Calculate the angular velocity of the ring 5 seconds after the torque is applied to the drum and the tension in the cable at O. Neglect all frictions В E 375 mm V1 = 1.2 m/sarrow_forward
- Please answer quickly! Thanksarrow_forwardThe slender L-shaped bar ABCD mass 15 kg/m is free to rotate about thepin at B. The spring connected to the bar at A has a free length of 7 ft, and itsstiffness is 180 N/m. If the system is released from rest in the position shown,determine the angular velocity of the bar when A is directly above B.arrow_forward1000 lb -8 ft +2ft A beam that weighs 300 lbs is supported by a roller and pin B and A respectively while being subjected to a force of 1000 lbs. If the pin at A is suddenly removed, determine the beams angular acceleration, the force exerted by support B and the horizontal acceleration just after A is removed. Assume the beam is a slender rod of negligible thickness. Please don't use angle measurements when solving. Use the 3-4-5 triangle to solve, if that makes sense. Thank you! Choutranco impgo toutarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY