
Fill in the blanks.
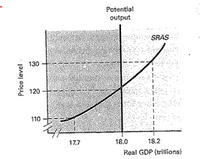
Answer questions a through d on the basis of the following graph:
a. If the actual
b. The situation described in part a result in a _________ gap equals to ____________.
c. If the actual price level is lower than the expected price level reflected in long term contracts, real GDP equals __________ and the actual price level equals ________ in the short run.
d. The situation described in part C result in a ________ gap equal to ___________
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

EXPANSIONARY AND RECESSIONARY GAPS Ans wer the following questions on the basis of the following graph:
If the actual
EXPANSIONARY AND RECESSIONARY GAPS Ans wer the following questions on the basis of the following graph:
If the actual
- Explain what changes in structural variables could lead to the larger quantities demanded and supplied while the equilibrium price stays at $4. Draw the relevant supply-demand diagram, which furnishes the coordinates of the DD and SS curves at the $4 price. Provide a detailed explanation of your diagram.arrow_forwardIn Exhibit 1, as production increases, firms resort to offering higher wage rates to attract the dwindling supply of unemployed resources in: Group of answer choices the segment labeled ab. the segment labeled bc. the segment labeled cd. both segment bc and segment cd. PreviousNextarrow_forward(23) Assume that the economy begins in long-run equilibrium and that the federal reserve decides to use open market operations to sell bonds. In the short run, what happens to the price level? Group of answer choices (A) It goes down. (B) It goes up. (C) It stays the same.arrow_forward
- Answer questions a through F on the basis of the following graph: a. If the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long term contracts, real GDP equals ____________ and the actual price level equals _________ in the short run. b. The situation described in part a result in a _________ gap equals to ____________. c. If the actual price level is lower than the expected price level reflected in long term contracts, real GDP equals __________ and the actual price level equals ________ in the short run. d. The situation described in part C result in a ________ gap equal to ___________arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forward“Members of Congress are interested in increasing the minimum wage from its current rate of $7.25 an hour to $15. What effect will this have on the unemployment rate for low-skilled workers? How is this likely to impact equilibrium output and the price level in the short run?"arrow_forward
- Consider the orginal IS-curve. Suppose demand in the U.S. for imports from Japan increases. This leads to what? Select all the correct statements. (a) Lower short - run output in the U.S.. (b) A downward shift in the IS - curve in Japan. (c) A positive aggregate demand shock in Japan. (d) An upward shift in the IS - curve in the U.S.. (e) A movement along the IS-curve in Japan.arrow_forwardA) Discuss, with examples, factors or events that might shift the short run aggregate supply curve. B) Imagine an economy is in long run equilibrium. Now suppose that firms experience an increase in their cost of production (say, due to a natural disaster). i. Explain, with graphs, the macroeconomic impact of such an increase in production costs. ii. Describe how policymakers could use fiscal policy to counteract the effects of increased cost of production.arrow_forwardAll of the following statements about sticky prices are true except: Select one: a. for studying year-to-year fluctuations, most macroeconomists believe that price stickiness is a better assumption than is price flexibility b. the sticky-price model describes the equilibrium toward which the economy slowly gravitates c. in the short run, some wages and prices are sticky d. magazine publishers tend to change their newsstand prices only every three to four yearsarrow_forward
- Subsidies: Governments can provide subsidies to businesses that are most affected by the supply shock. For example, if a sudden rise in the price of oil is causing higher transportation costs, governments can provide subsidies to help offset those costs. Explain that graphically please.arrow_forwardPart 2 Answer questions a through F on the basis of the following graph: e. If the actual price level equals the expected price level reflected in long term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals ________ in the short run. f. The situation described in part E result in a _________ gap equal to __________arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





