
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
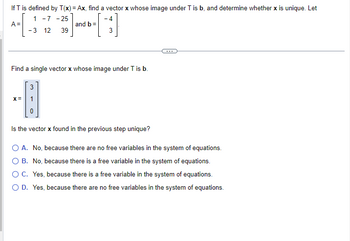
Transcribed Image Text:If T is defined by T(x) = Ax, find a vector x whose image under T is b, and determine whether x is unique. Let
A =
1 -7 -25
-3 12 39
and b =
-4
3
Find a single vector x whose image under T is b.
3
-A
X =
Is the vector x found in the previous step unique?
O A. No, because there are no free variables in the system of equations.
O B. No, because there is a free variable in the system of equations.
O C. Yes, because there is a free variable in the system of equations.
O D. Yes, because there are no free variables in the system of equations.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume that n(U)=90n(U)=90, n(A)=41n(A)=41, n(B′)=50n(B′)=50, and n(A∪B)=63n(A∪B)=63. Find n(A∩B)arrow_forwardSpent a lot of time solving it, need some helparrow_forwardDetermine whether b can be written as a linear combination of a₁, a2, and a3. In other words, determine whether weights X₁, X₂, and X3 exist, such that x, a₁ +X₂ª₂ +X3ª3 = b. Determine the weights X₁, X₂, and x3 if possible. ·0-0-0 2 a₂ 4 1 Let a₁ = 1 -3 O A. x₁ = 2, X₂ = 1, X3 = 2 O B. x₁=1, x₂ = 0, X3 = 1 OC. x₁ = -2, x2 = -1, x3 = -5 O D. There is no solution. 2 6 and b= 3 -5 -4arrow_forward
- B: Find the values x,y, and z in the following linear equations by using Cramer's rule: x+2y-2z = -1 -3x + 2y+z=4 2x-y+z= 3arrow_forwardUse Cramer's Rule to find values for x, y, and z that satisfy the following system. + 4z = 13 14 = -3 Answer: x = y = X -5y + 3z -x + 2y 7 and 2 = =arrow_forwardFind u - v, 2(u + 3v), and 2v – u. u = (2, 0, -8, 3), v = (0, 7, 3, 2) (a) u - v = (b) 2(u + 3v): (c) 2v – u =arrow_forward
- Let ā = (−1, 1, 3) and 6 = (0, -4, k). a Find k so that a and b will be orthogonal. k =arrow_forward3 13 Given A = - 4 - 12 - 4 observe that the first column plus twice the third column equals the second column, Find a nontrivial solution of Ax = 0 without -3 - 15 9- performing row operations. [Hint: Write Ax = 0 as a vector equation.] X =arrow_forward-3 in the forms A= LDL" and A=1, d, 1 +l,d215. Are the 5 1.3.1 Write A = -3 pivots positive, so that A is symmetric positive definite? Write 3x – 6x1 x2+ 5x as a sum of squares.arrow_forward
- Find u x v, v x u, and v × V. u = (-6, 2, -7) v = (-2, -5, -3) (a) 29i + 4j + 26k u x V (b) V x u -29i - 4j - 26k (c) 0 V X V ►arrow_forwardSolve this true/flase linear algebra question. Please show your work.arrow_forwardWrite a in the form a = a,T+a,N without finding T and N. r(t) = (2 + 8t)i + (t - 2)j – 8tk a=T-Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

