
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
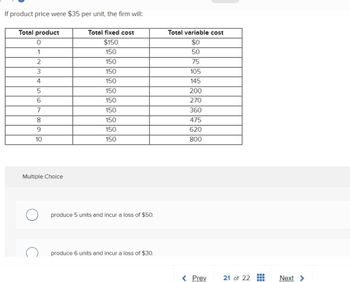
Transcribed Image Text:If product price were $35 per unit, the firm will:
Total product
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Multiple Choice
O
Total fixed cost
$150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
150
produce 5 units and incur a loss of $50.
produce 6 units and incur a loss of $30.
Total variable cost
$0
50
75
105
145
200
270
360
475
620
800
< Prev
21 of 22
‒‒‒
T
T
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given the following functions for shoe factory in Ohio: fi: Qa=2(90-P) 1 P==Qs 4 Where Q is quantity and P is price. fz given is the Marginal Cost for the shoe factory but this producer often dumps left over materials such as glues and dyes directly into the sewer effecting ground water in the nearby town. An expert in the field discovered that the marginal damage is a constant $9. 1. What is the social marginal cost (show all working)? 2. What is the new equilibrium when pollution damage is taken into consideration for this market? 3. What is the total surplus when accounting for the damages? (Evaluate at the SMC level) - Draw the diagram and label. 4. What is the Deadweight loss for the pollution in the event that the producers do not pay for the damages? (Identify the DWL on your diagram) 5. What is the Total Social Surplus taking damages into account?arrow_forwardIn the market for foam fire retardant there is only one firm. The demand func-tion for the product is Q = 15,000 – 10P where Q is the annual sales quantity in tons and P is the price per ton. The firm’s total cost function (in dollars) is C = 1,400,000 + 300Q + 0.05Q2.a) How much foam fire retardant should this firm produce and sell in order to maximize its profit? What price should it charge?b) Compute the firm’s total profit.c) Suppose now that the firm faces a 20% increase in variable costs. Determine what impact this will have on the firm’s optimal choice.arrow_forwardRent of a factory is the fixed cost for the firm True/Falsearrow_forward
- p=D(x)=71.5−0.02xp=D(x)=71.5−0.02x dollars. The total cost for these coffee makers is given by C(x)=0.05x2+5.5x+6200C(x)=0.05x2+5.5x+6200 dollars. Determine the marginal profit for 118 coffee makers.arrow_forwardfrom Profit = 144X – 3X² – XY – 2Y² + 120Y – 35 to get the Marginal profit of X = d(Profit)/dX X = 144 - 6X - Y show the complete solutionarrow_forwardPakPerfect Inc. estimates equation of its total costs of production as TC = 500 + 10Q + 5Q2 and market demand for its product as Qd = 105 – (1/2) P, where Q is quantity in units and P is price in Pak$. Write the equations of the firm’s costs, as a function of Q: Average Total Cost ATC Average Variable Cost AVC Average Fixed Cost AFC Given above costs can you determine what will be the firm’s production in Stage 1? What is the breakeven price and breakeven quantity for this firm? What is the shutdown price and quantity for this firm? Draw the firm’s costs in a graph as per your determination in (a). Label the breakeven and shutdown price and quantity using information in (b) and (c) above. Given the market price of Pak$ 50 how many units should the firm produce? how many firms are competing in this market in short-run? How many firms will be in the industry in the long-run? How do you interpret the profit or loss condition of PakPerfect? Use a two-panel graph of the Market and…arrow_forward
- (b) Formidable Manufacturing Company has the following cost functions in the short run, where production level, Q is measured in '000s of units: TC = 0.5Q³ – 2Q² + 5Q FC = 7 (i) Calculate the optimum output level for this company in the short run (ii) Calculate the marginal cost for this company at a production level of 2,500 units. (iii) The industry for in which Formidable Manufacturing Company operates classifies its members by the following output: Size Micro Small Medium Large Output (Q): 0-1000 1000-3000 3000-6000 >6000 In the long run, the AVC for this industry is given by: AVC = 0.4Q² – 3Q + 15. Determine the optimum plant size for this industry.arrow_forward(a) The marginal cost of two firms are given by the following | cost Firm 1: C'(Q) = 300e® 1Q+2 TC= 3000 when Q = 0 Firm 2: C'(Q) = 41 +30Q -5Q² TC =400 when Q = 0 (ii, (iii) avee (iv) Find the total cost for producing up to 100 unitsarrow_forwardThe Lead Zeppelin Company produces powered and steerable lighter-than-air craft. The company’s airships are specially lined and are therefore safer than normal dirigibles. The table below shows the weekly production of dirigibles, along with the associated Average Cost and Total Revenue figures (the Average Cost and Total Revenue figures are actually in thousands of dollars, so the $15 represents $15,000, but we have left off the zeros to save space). Quantity Average Cost Total Cost Total Revenue 0 -- 0 $0 1 $15 15 $10 2 $9 18 $20 3 $8 24 $30 4 $8.50 34 $40 5 $9 45 $50 6 $10 60 $60 7 $12 84 $70 The Lead Zeppelin Company has decided that it will produce at least 1 dirigible. Now the question becomes, how many more dirigibles should it produce to make as much profit as possible? Use the profit-maximizing rule to explain how many dirigibles the Lead Zeppelin Company should produce to…arrow_forward
- The Jones are small farmers in the wheat industry – they are price takers. Their cost function is: TC = 600,000 + 3,000Q + Q2 and MC = 3,000 + 2Q. The market price is $5,000 per ton. Assuming the Jones are maximizing profits (or minimizing loses), how much profit are they making? You must show your work.arrow_forwardA small tie shop finds that at a sales level of x ties per day its marginal profit is MP(x) dollars per tie, where MP(x)=1.40 +0.02x -0.0006x². Also, the shop will lose $75 per day at a sales level of x = 0. Find the profit from operating the shop at a sales level of x ties per day. P(x)=arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education