
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
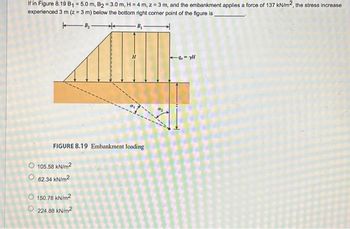
Transcribed Image Text:If in Figure 8.19 B₁ = 5.0 m, B₂=3.0 m, H = 4 m, z = 3 m, and the embankment applies a force of 137 kN/m2, the stress increase
experienced 3 m (z = 3 m) below the bottom right corner point of the figure is,
B₂-
**
FIGURE 8.19 Embankment loading
105.58 kN/m²
62.34 kN/m²
Ⓒ 150.78 kN/m²
Ⓒ224.88 kN/m²
-9-yl
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A long embankment 30 m wide is to be built on ground. The net vertical pressure applied by the embankment (assumed to be uniformly distributed) is 90kpa. The soil profile and stress distribution beneath the center of the embankment is also shown. The value of mv for the upper clay is 0.35m2/MN, and for the lower clay mv=0.13m2/MN. Tthe permeabilities of the cllays are 10-10m/s and 10-11m/s for the upper and lower soil respectively. Determine the final settlement under the center of the embankment due to consolidationarrow_forward*An embankment is proposed to construct on 10m thick clay deposit having the coefficient of volume compressibility as 2.7 x 10^-4 m?/kN. Determine the settlement of clay by the increase in vertical stress of 60 kN/m? due to the construction of embankment.arrow_forwardd 8.16 An irregularly shaped footing shown in the figure is loaded with 60 kN/m² uniform load on the ground. Compute the vertical stress increment under Point A at the depth z = 4 m. INTRODUC INT 5.0 m 5.0 m 15.0 m A 5.0 m r = 5.0 marrow_forward
- An embankment consists of clay fill for which c′ = 25 kN/m2 and φ = 27° (from consolidated undrained tests with pore-pressure measurement). The average bulk unit-weight of the fill is 2 Mg/m3. Estimate the shear-strength in kPa of the material on a horizontal plane at a point 20 m below the surface of the embankment, if the pore pressure at this point is 180 kN/m2 as shown by a piezometer.arrow_forwardFor the embankment shown in Figure 10.45, determine the vertical stress increases at points A, B, and Carrow_forwardThe figure shows a weir, the base of which is 6m below the ground. The necessary flow net has also been drawn assuming Kx = Kv = K. K = 0.005 m⁄sec. Compute the following: rate of seepage through the foundation in liters/sec. uplift pressure at“f”. uplift force per unit length measured along the axis of thearrow_forward
- 4. The masonry dam shown below has a crest width of 2m, base width of 15.0 m, and a height of 20m. Masonry weighs 23.54 kN/m³. If the allowable compressive stress at the toe is 345 kN/m², what is the permissible depth of the headwater? Assume there is no hydrostatic uplift. 2 m Elev. 8 m (crest) W.S. h/3 Elev. 0 m (base) Тое 15 marrow_forward(Use The Figure (10.20) to find the solution of this question) Two embankments loads on silty clay soils layers as shown below. Unit weights of the left and right embankments are 11 and 13 kN/m², respectively. Determine the stress increase under the embankments at point A that are loaded at a depth of 4 m below the ground surface. Center ine 1V:1H y= 11 kN/m 5m 13 N/m Figure 10.19 Embankment loading 050 3.0 20 045 14 12 LO 0.40 09 07 0.35 06 0.30 04 025 020 02 a10 Figure 10.20 Osterberg's chart for determination of vertical stress 0.00 TT TT due to embank- 100 ment koading 327 HEAIarrow_forwardSubject: Soil Mechanicsarrow_forward
- A building is founded on a rectangular mat of dimensions 20 m x 10 m as shown in the plan view in figure below. A surcharge of 300 kPa is applied within the area ABCD whereas a surcharge of 100 kPa is applied within the area CDEF. Calculate the increase in vertical total stress in kPa at the depth of 5 m below Point Farrow_forwarda= 5arrow_forward2 A granular soil is subjected to a minor principal stress of 200 kN/m². If the angle of internal friction is 30°, determine the inclination of the plane of failure with respect to the direction of the major principal stress. What are the stresses on the plane of failure and the maximum shear stress induced? 3 An embankment consists of clay fill for which c' 25 kN/m2 and o = 27° (from consolidatedundrained tests with pore-pressure measurement). The average bulk unit-weight of the fill is 2 Mg/m'. Estimate the shear- strength of the material on a horizontal plane at a point 20 m below the surface of the embankment, if the pore pressure at this point is 180 kN/m² as shown by a piezometer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning