
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
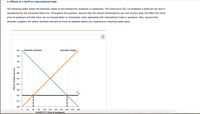
Transcribed Image Text:4. Effects of a tariff on international trade
The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for soybeans in Guatemala. The world price (Pw) of soybeans is $550 per ton and is
represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world
price of soybeans and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in soybeans. Also, assume that
domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place.
830
Domestic Demand
Domestic Supply
795
760
725
O 690
655
620
585
Pw
550
515
480
30
60
06
120 150 180
210
240
270
300
QUANTITY (Tons of soybeans)
PRICE (Dollars per ton)

Transcribed Image Text:If Guatemala is open to international trade in soybeans without any restrictions, it will import
tons of soybeans.
Suppose the Guatemalan government wants to reduce imports to exactly 60 tons of soybeans to help domestic producers. A tariff of $
per
ton will achieve this.
A tariff set at this level would raise
in revenue for the Guatemalan government.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q3: Using a domestic-market demand- and supply-curve graph, show the impact of tariff on a small country's import price, domestic demand, domestic supply, import quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, government revenue, and total welfare; Is the country unambiguously worse off as a result of the tariff? In the same graph, show how to achieve the same import quantity with an import quota; When would the tariff and the import quota lead to the same amount of welfare change? How will the answer to (a) and (b) change if the country uses a subsidy that is equivalent to the tariff rate to help domestic producers? How would the answers to (a) and (b) change for a large country? Your answer:arrow_forwardAnalyze the impact of the tariff on domestic production, consumption, and imports of solar panels. Include a graph with properly labeled axes, demand and supply curves, and tariff levels to illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardKazakhstan is a grape producer, as well as an importer of grapes. Suppose the following graph shows Kazakhstan's domestic market for grapes, where SK is the supply curve and DK is the demand curve. The free trade world price of grapes (Pw) is $800 per ton. Suppose Kazakhstan's government restricts imports of grapes to 60,000 tons. The world price of grapes is not affected by the quota. Analyze the effects of the quota on Kazakhstan's welfare. On the following graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to draw the Kazakhstan's supply curve including the quota Sk+Q. (Hint: Draw this as a straight line even though this curve should be equivalent to the domestic supply curve below the world price.) Then use the grey line (star symbol) to indicate the new price of grapes with a quota of 60,000 grapes. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 0 20 SK K P W 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons) SK+Q The equivalent import tariff for…arrow_forward
- Country X has 100 units of labour and country Y has 200 units of labour. Both countries produce computers and televisions. The unit labour requirements are given in the table below: Computers Televisions Country X 50 Country Y 100 Assume that free trade exists and that the relative price is such that both countries specialize completely in the industry in which they have a comparative advantage (neither country produces both goods). The supply of computers relative to televisions will be Select one: a. 0.02 (or 1/50) O b. 0.013 (or 1/75) c. 0.01 (or 1/100) d. impossible to determine without knowing the relative price of computers in terms of televisionsarrow_forwardKazakhstan is a grape producer, as well as an importer of grapes. Suppose the following graph shows Kazakhstan's domestic market for grapes, where SK is the supply curve and Dk is the demand curve. The free trade world price of grapes (Pw) is $800 per ton. Suppose Kazakhstan's government restricts imports of grapes to 120,000 tons. The world price of grapes is not affected by the quota. Analyze the effects of the quota on Kazakhstan's welfare. On the following graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to draw the Kazakhstan's supply curve including the quota SK+Q. (Hint: Draw this as a straight line even though this curve should be equivalent to the domestic supply curve below the world price.) Then use the grey line (star symbol) to indicate the new price of grapes with a quota of 120,000 grapes. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 0 40 80 120 160 200 SK 240 10 0² W 280 320 360 400 SK+Q Price with Quota A Change in PS Quota Rents DWL ?arrow_forwardRefer to the graph below of a large country that has imposed a tarifft on this good. The terms-of-trade gain for this country is , and the deadweight loss suffered by this country is Price $36 $30 $26 Home market S D 20 40 80 100 Quantity Price World market 40 80 Importsarrow_forward
- Home's demand curve for wheat is P = 10 - (1/20)Qd. Its supply curve is P = 4+ (1/20)Qs Foreign's demand curve for wheat is P * = 8 - (1/20) Qd* Its supply curve is P* = 2+(1/20)Qs* Determine the effect of the tariff on Home import-competing producers APS = Home consumers ACS = Home government tariff revenue AGR= Adding these effects together AWAPS + ACS + AGR =arrow_forwardEconomics Questionarrow_forwardConsider the pharmaceutical market in the US. The demand is Q = 200 - 2P Q P while supply is 2 40s Q P. The free trade price is 25. A) Calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, total surplus, and imports under free trade. Illustrate all of these on a fully labelled graph. B) Suppose that the US puts a tariff of 6 on pharmaceuticals. When it does this, the free trade prices falls to 24. Calculate consumer surplus, producer surplus, tariff revenues, total surplus and deadweight loss under the tariff. Illustrate all of these on a fully labelled graph. C) Is the country better off under the tariff or free trade? How do you know?arrow_forward
- All of the following statements about import tariffs are true except Group of answer choices they result in countries selling the product at a lower price to domestic consumers they reduce the volume of trade and the gains from trade they limit specialization and the division of labor they yield revenue for the government that levies tariffsarrow_forwardChina placed tariffs on the importation of US soybeans. Assume that the domestic market for soybeans in China is described by the following equations: Demand: P = 11.5 – Q Supply: P = 5.5 + Q Price is in 10 Yuan (¥) per bushel of soybeans and the units for Quantity are 100 million bushels per year. This is to make graphing simpler. This does NOT mean that the price is 10 and quantity is 100. Rather it means that if the price was 40¥ and the quantity was 7,500,000,000 bushels, this would plot as 4 and 7.5 respectively. The world price for soybeans is ¥65/bushel (this would graph as a horizontal line at 6.5). Graph the soybean market in China showing equilibrium both with no barriers to trade and with a ¥15/bushel tariff. Be sure to fully and clearly label the graph including: Domestic Demand curve (D), Domestic Supply curve (S), the World Price (WP), and the Price with tariffs (PT), along with the quantities imported both with and without the tariff. Based on your graph, what…arrow_forward5. Agricultural export subsidies in a small nation The following graph shows the market for wheat in Canada, where Do is the demand curve, Sc is the supply curve, and Pw is the free trade price of wheat. Assume that Canada is a relatively small producer of wheat, so changes in its output do not affect the world price of wheat. Also assume that Canada is currently open to free trade, and domestic consumers are able to purchase wheat at the world price with negligible transportation costs. Suppose a subsidy of $80 per ton is granted to exporters in Canada, allowing them to sell their products abroad at prices below their costs. Assume that trade restrictions are also put in place in order to prevent domestic consumers from buying wheat abroad at the world price. Use the grey line (star symbols) to indicate the world price of wheat plus the subsidy on the following graph. Then use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the price of wheat in Canada and the quantity demanded at that…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education