
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781337395083
Author: Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Financial Accounting Question please answer
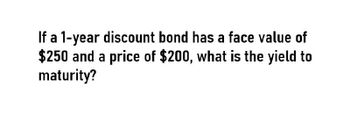
Transcribed Image Text:If a 1-year discount bond has a face value of
$250 and a price of $200, what is the yield to
maturity?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is interest rate (or price) risk? Which bondhas more interest rate risk: an annual payment1-year bond or a 10-year bond? Why?arrow_forwardSuppose you purchase bond that has a coupon of $75 face value of $1000 and current price of $1000 what is your coupon rate?what is your current yield?arrow_forwardWhat relationship between the required return (ytm) and the coupon interest will cause a bond to: a) Be priced at a discount¿ FALL2022 b) Be priced at a premium? c) Be priced at its par value?arrow_forward
- d. If you hold the bonds for one year, and interest rates do not change, what total rate of return will you earn, assuming that you pay the market price? Why is this different from the current yield and YTM?arrow_forwardWhich is generally considered the more appropriate estimate ofthe risk-free rate: the yield on a short-term T-bill or the yield on a10-year T-bond?arrow_forwardWhat is the stand-alone risk? Use the scenario data to calculate the standard deviation of the bonds return for the next year.arrow_forward
- The current zero-coupon yield curve for risk-free bonds is as follows What is the price per $100 face value of a two-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond? The price per $100 face value of the two-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond is $ ____ (Round to the nearest cent.)arrow_forwardWhich of the following is correct? O If you pay a price above its face value to buy a bond, your return will be higher than its coupon rate. O When market rate is greater than coupon rate, the bond has a price below its face value. O When determining the value of a bond that payments semi-annual payments, one need to use semi-annual coupon rate to determine the coupon payments and semi-annual market rate as discount rate.arrow_forwardAssume that the real risk-free rate is 2% and the average annual expected inflation rate is 4%. The DRP and LP for Bond A are each 2%, and the applicable MRP is 3%. What is Bond A's interest rate?arrow_forward
- Suppose that y is the yield on a perpetual government bond that pays interest at the rate of $1 per annum. Assume that y is expressed with simply com- pounding, that interest is paid annually on the bond, and that y follows the process dy = a(y0 −y)dt + oydWt, where a, y0, and o are positive constants and dWt is a Wiener process. (a) What is the process followed by the bond price? (b) What is the expected instantaneous return (including interest and capital gains) to the holder of the bond?arrow_forwardConsider a bond with a face value of $1000. An increase and decrease in 1 bp results in the price changing to 995.12707 and 996.09333, respectively. What is its PVBP?arrow_forwardSuppose 2-year Treasury bonds yield 4.1%,while 1-year bonds yield 3.2%. r* is 1%, and the maturity risk premium is zero.a. Using the expectations theory, what is the yield on a 1-year bond, 1 year from now?Calculate the yield using a geometric average.b. What is the expected inflation rate in Year 1? Year 2?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning