
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
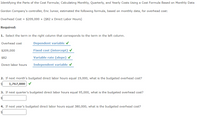
Transcribed Image Text:Identifying the Parts of the Cost Formula; Calculating Monthly, Quarterly, and Yearly Costs Using a Cost Formula Based on Monthly Data
Gordon Company's controller, Eric Junior, estimated the following formula, based on monthly data, for overhead cost:
Overhead Cost = $209,000 + ($82 x Direct Labor Hours)
Required:
1. Select the term in the right column that corresponds to the term in the left column.
Overhead cost
Dependent variable v
$209,000
Fixed cost (intercept) v
$82
Variable rate (slope)
Direct labor hours
Independent variable v
2. If next month's budgeted direct labor hours equal 19,000, what is the budgeted overhead cost?
1,767,000 V
3. If next quarter's budgeted direct labor hours equal 95,000, what is the budgeted overhead cost?
4. If next year's budgeted direct labor hours equal 380,000, what is the budgeted overhead cost?
$
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The "x" in the overhead cost equation, y = $5.50x + $92,000, represents which of the following? total overhead costs. the variable costs. total fixed costs. the cost driver in units.arrow_forwardValaarrow_forwardEvaluating Selected Cost Driver Assume that a manufacturer of specialized machine parts developed the following total cost estimating equation for manufacturing costs. Y = $14,400 + $1,250 (actual units) a. What is total estimated manufacturing costs if 180 units are produced? $Answer 0arrow_forward
- Given the following cost and activity observations for Bounty Company's utilities, use the high-low method to determine Bounty's variable utilities cost per machine hour. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Cost Machine Hours March $3,142 15,489 April 2,691 10,041 May 2,810 11,509 4 June 3,881 18,009 a. $0.15 b. $1.05 O c. $1.64 Od. $1.01 10:21 PM 670002 K 63°Farrow_forwardThe managing director of a consulting group has the accompanying monthly data on total overhead costs and professional labor hours to bill to clients. Complete parts a through c. Click the icon to view the monthly data. a. Develop a simple linear regression model between billable hours and overhead costs. Overhead Costs = +xBillable Hours X Monthly Overhead Costs and Billable Hours Data (Round the constant to one decimal place as needed. Round the coefficient to four decimal places as needed. Do not include the $ symbol in your answers.) Overhead Costs Billable Hours 0 $315,000 3,000 $365,000 4,000 $395,000 5,000 $447,000 6,000 $530,000 7,000 $550,000 8,000arrow_forwardDeidoro Company has provided the following data for maintenance cost: Machine hours Maintenance cost Multiple Choice Maintenance cost is a mixed cost with variable and fixed components. The fixed and variable components of maintenance cost are closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) O O Prior Year 17,100 20,100 $ 29,400 $ 34,200 $29,400 per year; $1.701 per machine hour Current Year $2,040 per year; $1.701 per machine hour $2,040 per year; $1.600 per machine hour $29,400 per year; $1.600 per machine hourarrow_forward
- Provide answer this questionarrow_forwardMenk Corporation has provided the following information: Cost per Unit Cost per Period Direct materials $ 6.80 Direct labor $ 3.80 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 2.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 20,200 Sales commissions $ 0.50 Variable administrative expense $ 0.40 Fixed selling and administrative expense $ 10,100 Required: a. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the variable cost per unit sold? Note: Round "Per unit" answer to 2 decimal places. b. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the total amount of variable costs related to the units sold? c. If 5,220 units are produced, what is the total amount of manufacturing overhead cost incurred? a. Variable cost per unit sold b. Total variable costs c. Total manufacturing overhead costarrow_forwardTom’s Shoe Repair provides a variety of shoe and repair services. Analysis of monthly costs revealed the following cost formulas when direct labor hours are used as the basis of cost determination: Supplies: y = $0 + $4.00X Production supervision and direct labor: y = $500 + $7.00X Utilities: y = $350 + $5.40X Rent: y = $450 + $0.00X Advertising: y = $75 + $0.00X a. Prepare a flexible budget at 250, 300, 350, and 400 direct labor hours. b. Calculate a total cost per direct labor hour at each level of activity. c. Tom’s employees usually work 350 direct labor hours per month. The average shoe repair requires 1.25 labor hours to complete. Tom wants to earn a 40 percent margin on his cost. What should be the average charge per customer, rounded to the nearest dollar to achieve Tom’s profit objective?arrow_forward
- Determine fixed and variable costs using the high-low method and prepare graph. E2.26 (LO 3) The controller of Furgee Industries has collected the following monthly expense data for use in analyzing the cost behaviour of maintenance costs. Total Maintenance Costs Total Machine Hours Month January February March April May June $2,500 3,000 3,600 4,500 3,200 4,900 300 350 500 690 400 700 Instructions a. Determine the fixed and variable cost components using the high-low method. b. Prepare a graph showing the behaviour of maintenance costs, and identify the fixed and variable cost components. Use 100-hour increments and $1,000 cost increments.arrow_forwardConnell Co. collects the following data concerning a mixed cost, using miles as the activity level. Miles Driven Total Cost January 10,000 $17,000 February 8,000 $13,500 March 9,000 $14,400 April 7,000 $12,500 Instructions: Compute the variable and fixed cost elements using the high-low method.arrow_forwardBruno Company accumulates the following data concerning a mixed cost, using miles as the activity level. Miles Driven Total Cost January 8,015 February 7,510 $14,195 13,515 Miles Driven Total Cost March 8,500 $15,000 April 8,205 14,495 a. Compute the variable cost per mile using the high-low method. b. Compute the fixed cost elements using the high-low method.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education