
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
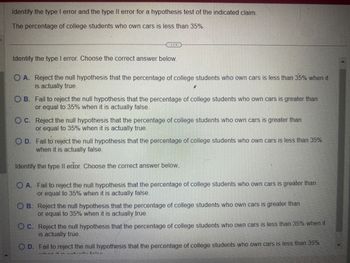
Transcribed Image Text:Identify the type I error and the type II error for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim.
The percentage of college students who own cars is less than 35%.
Identify the type I error. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is less than 35% when it
is actually true.
2
OB. Fail to reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is greater than
or equal to 35% when it is actually false.
OC. Reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is greater than
or equal to 35% when it is actually true.
O D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is less than 35%
when it is actually false.
Identify the type II erfor. Choose the correct answer below...
O A. Fail to reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is greater than
or equal to 35% when it is actually false.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is greater than
or equal to 35% when it is actually true.
C.
Reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is less than 35% when it
is actually true
O D. Fail to reject the null hypothesis that the percentage of college students who own cars is less than 35%
*..këm ¡4 :-
2.
„, fele-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine the second step of hypothesis testing, and explain the procedure and logic of this step. Choose the correct answer below. A. The second step is to figure out the probability of getting a particular result if the research hypothesis is true. In this process, one wants to determine the probability of getting a sample score as extreme as the one found if the sample were from a population with a distribution corresponding to the research hypothesis being true. B. The second step is to determine if the test should use a directional hypothesis or a nondirectional hypothesis. Once this is determined, the correct cutoff sample scores can be obtained. C. The second step is to determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution. The overall logic of hypothesis testing involves figuring out the probability of getting a particular result if the null hypothesis is true. In this process, one wants to determine the probability of getting a sample score as…arrow_forwardDo a hypothesis for the following, make sure to include and label all five steps: Test the claim that tutoring influences a student’s test scores. Use a 0.01 level of significance. Use the following before and after scores for 5 students. Before 78 79 65 78 68 After 85 83 62 85 79arrow_forwardFill in the blank. The The is a value used in making a decision about the null hypothesis and is found by converting the sample statistic to a score with the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. is a value used in making a decision about the null hypothesis and is found by converting the sample statistic to a score with the assumption that the null hypothesis is true.arrow_forward
- In a study of 819 randomly selected medical malpractice lawsuits, it was found that 473 of them were dropped or dismissed. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that most medical malpractice lawsuits are dropped or dismissed. Which of the following is the hypothesis test to be conducted? ОА. Но: р30.5 H;: p> 0.5 ОС. Но: р0.5 H1: p= 0.5 OF. Ho: p= 0.5 ОЕ. Но: р-0.5 H1: p#0.5 H1: p<0.5 What is the test statistic? (Round to two decimal places as needed.) What is the P-value? P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardDescribe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim. A police station publicizes that at least 60% of applicants become police officers. Describe the type I error. Choose the correct answer below. O A. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of applicants who become police officers is at most 0.60, but you reject Ho: p≤0.60. O B. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of applicants who become police officers is at least 0.60, but you reject Ho: p20.60. OC. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of applicants who become police officers is at most 0.60, but you fail to reject H₁: p≤0.60. OD. A type I error will occur when the actual proportion of applicants who become police officers is at least 0.60, but you fail to reject Ho: p² 0.60. Describe the type II error. Choose the correct answer below. O A. A type Il error will occur when the actual proportion of applicants who becomepolice officers is less than 0.60, but you…arrow_forwardThe P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Ho when the level of significance is (a) a = 0.01, (b) a = 0.05, and (c) a = 0.10. P= 0.0158 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.01 level of significance? O A. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.0158, is greater than a = 0.01. O B. Fail to reject H, because the P-value, 0.0158, is greater than a = 0.01. O C. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0158, is less than a = 0.01. O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0158, is less than g = 0.01. (b) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.05 level of significance?arrow_forward
- 22. See photoarrow_forwardThe mean entry-level salary for an employee at a company is $40,000. You believe it is lower for entry-level IT professionals in the company.1. Identify the null hypothesis. 2. Identify the alternative hypothesis. 3. Identify the type I error. A. You decide that the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is $40,000, when, in actuality, the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is $40,000. B. You decide that the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is $40,000, when, in actuality, the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is lower than $40,000. C. You decide that the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is lower than $40,000, when, in actuality, the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is $40,000. D. You decide that the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is lower than $40,000, when, in actuality, the mean entry-level salary for IT professionals is lower than $40,000. 4. Identify the type II error. A. You decide that…arrow_forwardThe P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Ho when the level of significance is (a) a = 0.01, (b) a = 0.05, and (c) a = 0.10. P=0.1162 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject H, at the 0.01 level of significance? O A. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.1162, is greater than a = 0.01. O B. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.1162, is less than a= 0.01. O C. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.1162, is less than a= 0.01. O D. Fail to reject H, because the P-value, 0.1162, is greater than a = 0.01. (b) Do you reject or fail to reject H, at the 0.05 level of significance? O A. Fail to reject H, because the P-value, 0.1162, is less than a = 0.05. O B. Reject Họ because the P-value, 0.1162, is greater than a = 0.05. O C. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.1162, is greater than a = 0.05. O D. Reject H, because the P-value, 0.1162, is less than oa = 0.05. (c) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.10 level of significance? O A. Reject H,…arrow_forward
- Claim: Most adults would erase all of their personal information online if they could. A software firm survey of 640 randomly selected adults showed that 99.3% of them would erase all of their personal information online if they could. Make a subjective estimate to decide whether the results are significantly low or significantly high, then state a conclusion about the original claim.arrow_forwardNeed help with C , D and H pleasearrow_forwarduse a hypothesis test to determine if the proportions are statistically different. A recent survey showed that in a sample of 100 elementary school teachers, 15 were single. In a sample of 180high school teachers, 36 were single. Is the proportion of high school teachers who were single greater than theproportion of elementary teachers who were single? Use ΅ = 0.01.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman