
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
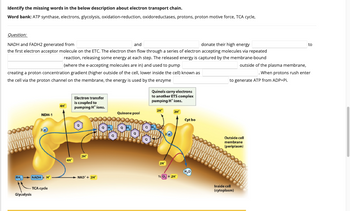
Transcribed Image Text:Identify the missing words in the below description about electron transport chain.
Word bank: ATP synthase, electrons, glycolysis, oxidation-reduction, oxidoreductases, protons, proton motive force, TCA cycle,
Question:
NADH and FADH2 generated from
and
donate their high energy
the first electron acceptor molecule on the ETC. The electron then flow through a series of electron accepting molecules via repeated
reaction, releasing some energy at each step. The released energy is captured by the membrane-bound
(where the e-accepting molecules are in) and used to pump
creating a proton concentration gradient (higher outside of the cell, lower inside the cell) known as
the cell via the proton channel on the membrane, the energy is used by the enzyme
RH
Glycolysis
NDH-1
NADH+H
TCA cycle
4H¹
4H
Electron transfer
is coupled to
pumping H* ions.
2H
NAD + 2H*
Quinone pool
Quinols carry electrons
to another ETS complex
pumping H* ions.
2H*
Wan
SIGH
2H
2H*
½20₂ + 2H*
Cyt bo
to generate ATP from ADP+Pi.
outside of the plasma membrane,
. When protons rush enter
Outside cell
membrane
(periplasm)
Inside cell
(cytoplasm)
to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The electron transport chain is... Group of answer choices A series of successive redox reactions A set of reactions occurring at the plasma membrane of mammalian cells used to produce NADH and FADH2 a series of phosphoryl-transfer reactionsarrow_forwardDetermine the total yield of ATP for the complete oxidation of 1 molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate. Show the work and reasoning, and indicate how many ATP, NADH, and FADH2 are formed and in which steps. Include ATP produced in the electron transport chain. Express the answer as a rangearrow_forwardThroughout the electron transport chain many reactions occur. What happens to NADH eventually? NADH is reduced NADH is not used in ETC. ONADH remains unchanged in ETC but is used later. ONADH is oxidizedarrow_forward
- ATP is an important molecule in cellular energetics. Which of the following statements is false? ATP hydrolysis can provide the energy required for mechanical work in a cell. All of the ATP made during cellular respiration is made by the enzyme ATP synthase. ATP synthesis is an endergonic reaction. None of the other answers are false.arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forwardChemiosmosis is a part of oxidative phosphorylation, the final step in cellular respiration. Which of the following is TRUE regarding chemiosmosis? ATP synthesis creates a proton gradient that causes electron flow through an electron transport chain (ETC). A temperature gradient drives ATP synthesis. The energy from a proton gradient is used to make ATP. Chemiosmosis regenerates electron carriers like NADH and FADH2.arrow_forward
- Complete the sentences to explain how the phosphorylation of ADP occurs. Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. ADP molecules High-energy move through phosphate molecule movement releases energy to combine a intermembrane space ATP synthase H+ ions CoQ mitochondrial matrix to return to the with ADP. Reset This Helparrow_forwardExplain the electron transport chain. You must know the reactants, products and location for each step.arrow_forwardWhich of the below cellular processes requires input of ATP energy? Group of answer choices ATP-synthase creating ATP Na+-K+-ATPase (sodium-potassium pump) activity Simple diffusion Pyruvate Oxidation The Electron Transport Chainarrow_forward
- In glycolysis, identify the enzyme and type of reaction (REDOX/group transfer/C-C make it or break it/isomerization/etc) that: -requires energy input form ATP (name one) -reduce NAD+ -are essentially irreversible in the cell (name 2) -is the committed steparrow_forwardIntermembrane Space Protein Complex of Electron H Carriers ATP Synthase Cyt C NADH NAD FADH FAD 2H + ,0, H,0 Mitochondrial Matrix ADP+ ATP Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis Oxidative Phosphorylation 19- Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? 20. Because they lose their mitochondria during development, red blood cells cannot perform aerobic respiration; however, they do perform glycolysis in the cytoplasm. Why do all cells need an energy source, and what would happen if glycolysis were blocked in a red blood cell? 21. What is the primary difference between a circular pathway and a linear pathway? 22. How do the roles of ubiquinone and cytochrome c differ from the roles of the other components of the electron transport chain? 23. What accounts for the different number of ATP molecules…arrow_forwardDescribe the oxidative phosphorylation/electron transport chain. Be sure to include all components and its location.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education