
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
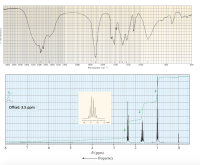
Identify each of the following compound (C4H8O2) from its molecular formula and its IR and 1H NMR spectra: Note: Offset means: “add “offset to 8 ppm.”Assign the peaks in NMR spectrum. You must indicate clearly the hydrogen/s of the molecule responsible for the peak/s.
Cannot write only the structure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A compound and its ¹H-NMR spectrum are shown below. Assign peak 1 and peak 2 in the spectrum to the hydrogen(s) labeled in red. i. a H3C- 10 C4H8O₂ Compound C b c -O—CH,CH3 2006 Brooks/Cole Thomson Submit Answer C 9 ↑ Which labeled hydrogen(s) correspond to each peak? peak 1: peak 2: 8 7 6 2H 5 Chemical Shift (8) Peak 3 Retry Entire Group 6 more group attempts remaining 3. 3H Peak 2 3H Peak 1 0 ppmarrow_forwardSteps in Spectral Identification: •Identify major peaks in IR spectrum, if any. •Deduce structural fragments for each of the 1H NMR spectral signals. •Give the structure of the compound •Assign the signals in the 1H NMR spectra to specific protons •Assign carbons to the peaks in the 13C NMR spectrum Step 1. Calculate the degree of unsaturation for the unknown. Step 2. Determine the functional group from IR Step 3. Analyzing the MS spectrum Step 4. Analyzing the 1H NMR spectra Determine the number of different kinds of protons Step 5. Analyzing the 13C NMR spectraarrow_forwardI need help with analyzing thisarrow_forward
- Need help, please.arrow_forwardThe proton NMR and IR spectra of an unknown compounds is shown on the next page. Using the molecular formula C5H12O, find L a) the index of saturation b) the structure of the unknown compound c) assign the absorption bands to the functional groups in the IR spectrum d) label all peaks in the NMR spectrum, and label the same peak on the hydrogens in the structure Transmittance (%) 100 80 60 40 20 0 3500 CT TYCE Tabdf62 2874.30 2500 Wavenumber (cm-¹) 3000 2000 1466.09 1500 1307.78 1124.04 21 seser 908.46 1000 37.21arrow_forward1. How would you differentiate between the following sets of molecules by IR and ¹H NMR? Consider: IR frequency and shape/intensity and NMR chemical shift, integration, and splitting. (There are multiple ways for each, but I am looking the 'blinding headlights' clue that would jump out at you.) VS CI OH VS VS ai i VS OH VS OHarrow_forward
- Determine the compound (name or structure) from the data. Explain features from each data. Molecular formula: C6H5Br Use molecular formula to determine IHD IR: Identify the presence/absence of five key functional groups NMR: Analyze this last. Consider multiplicity and peak area to confirm compound. The 5 H peak area covers both peaks (at 7.1 and 7.5 ppm Structure?arrow_forwardWhich of these choices best describes the interpretation of the following peak that may be recorded in a 'H NMR spectrum? 2.5 8 (2H, d). The underlined hydrogen atom is intended to be the one producing the peak that we are interpreting. O=C-CH,CO2H O=C-CH2CHX2 O=C-CH2CH2X O=C-CH2CH3 None of these interpretations describes this peak.arrow_forwardSteps in Spectral Identification: •Identify major peaks in IR spectrum, if any. •Deduce structural fragments for each of the 1H NMR spectral signals. •Give the structure of the compound •Assign the signals in the 1H NMR spectra to specific protons •Assign carbons to the peaks in the 13C NMR spectrum Step 1. Calculate the degree of unsaturation for the unknown. Step 2. Determine the functional group from IR Step 3. Analyzing the MS spectrum Step 4. Analyzing the 1H NMR spectra Determine the number of different kinds of protons Step 5. Analyzing the 13C NMR spectraarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY