
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
I need to write a SELECT query in SQL using these instructions. Attached is the code that created the tables.
SHOW name-of-tech part which are less than $300 and The Name of the Supplier. This will show which supplier has what parts under $300.
FOR [Supplier]
QUERY WILL USE: JOIN yes SUBQUERY no AGGREGATION no
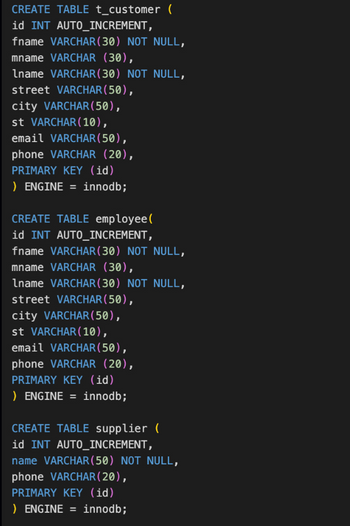
Transcribed Image Text:### Database Table Creation Scripts
The following SQL scripts are used to create three different tables in a relational database: `t_customer`, `employee`, and `supplier`. Each table is designed with specific fields and constraints to store relevant data efficiently.
---
#### `t_customer` Table
This table is designed to store customer information. The columns include:
- `id`: An integer that auto-increments to provide a unique identifier for each customer. It serves as the primary key.
- `fname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the customer's first name. This field is mandatory (NOT NULL).
- `mname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the customer's middle name.
- `lname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the customer's last name. This field is mandatory (NOT NULL).
- `street`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the street address of the customer.
- `city`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the city of the customer.
- `st`: A `VARCHAR(10)` field for the state of the customer.
- `email`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the customer's email address.
- `phone`: A `VARCHAR(20)` field for the customer's phone number.
The table uses the `InnoDB` storage engine.
---
#### `employee` Table
This table is designed to store employee information. The columns are:
- `id`: An auto-incrementing integer serving as the primary key.
- `fname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the employee's first name. This field is mandatory (NOT NULL).
- `mname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the employee's middle name.
- `lname`: A `VARCHAR(30)` field for the employee's last name. This field is mandatory (NOT NULL).
- `street`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the street address of the employee.
- `city`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the city of the employee.
- `st`: A `VARCHAR(10)` field for the state of the employee.
- `email`: A `VARCHAR(50)` field for the employee's email address.
- `phone`: A `VARCHAR(20)` field for the employee's phone number.
The table uses the `InnoDB` storage engine.
---
#### `supplier` Table
This table is tailored to store supplier information with the following fields:
- `id`: An auto

Transcribed Image Text:The image contains SQL code for creating three tables in a database, each designed to manage different aspects of a tech and customer management system.
### Table 1: `tech_parts`
- **Description:** Stores information about tech parts.
- **Columns:**
- `id`: INT, auto-increment, primary key
- `part_number`: INT, not null
- `name`: VARCHAR(30), not null
- `brand`: VARCHAR(30)
- `price`: INT
- `bought_date`: DATE
- `cus_id`: INT, foreign key referencing `t_customer(id)`
- `sup_id`: INT, foreign key referencing `supplier(id)`
### Table 2: `product`
- **Description:** Stores information about products.
- **Columns:**
- `id`: INT, auto-increment, primary key
- `brand`: VARCHAR(30)
- `devicetype`: VARCHAR(30)
- `cus_id`: INT, not null, foreign key referencing `t_customer(id)`
- `emp_id`: INT, not null, foreign key referencing `employee(id)`
- `part_id`: INT, foreign key referencing `tech_parts(id)`
### Table 3: `refurbished_item`
- **Description:** Stores information about refurbished items.
- **Columns:**
- `id`: INT, auto-increment, primary key
- `item_source`: VARCHAR(30), not null
- `brand`: VARCHAR(30)
- `device_type`: VARCHAR(30)
- `price`: INT
- `t_customer_id`: INT, not null, foreign key referencing `t_customer(id)`
- `employee_id`: INT, not null, foreign key referencing `employee(id)`
### Additional Information:
- All tables use `InnoDB` as their storage engine.
- Foreign keys ensure referential integrity between tables, linking customers and suppliers with their respective tech parts, products, and employees.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Based on stage 2, write queries for the following questions: Write a query to display all vendors sorted by vendor name. Write a query to display the product id, description, type, base, category, and price for all products that have a product base of water and a product category of sealer. Write a query to display the first name, last name, and email address of employees who were not hired from January 1, 2015, to December 31, 2019. Sort the output by the last name and then by the first name. Write a query to display the first name, last name, phone number, title, and department number of employees who work in department 123 and have the title “Assistant.” Write a query to display the employee number, last name, first name, salary “from” date, salary end date, and salary amount for employees 99675, 53845, and 44035. Sort the output by employee number and salary “from” date. Write a query to display the first name, last name, street no, street name, city,…arrow_forwardPlease help, I know it's hard but no one else is willing to try and I am lost and spent three days on this so far. Write a query to display the author ID, first and last name for all authors who have ever written a book with the subject Programming. Sort the results by author's last name (Figure P7.106). In the SQL Query do the following Select clause: Display the columns stated in the problem statement From clause: AUTHOR table Where clause: authors who have ever written a book with the subject Programming. (Hint: Subquery) Order by clause: Sort the results by author last namearrow_forwardplease assist with the following questions. need to write a syntax in SQL server. Create an UPDATE trigger called tr_check_qty on the OrderDetails table to prevent the updating of the quantity in the OrderDetails table if the quantity amount is greater than the units in stock in the Products table.arrow_forward
- What use cases are best suited for the CROSS APPLY function in SQL?arrow_forwardWrite all the sql code (including create, insert and select)arrow_forwardThe given SQL creates a Movie table and inserts some movies. The SELECT statement selects all movies. Press the Run button to produce a result table. Verify the result table displays five movies. Modify the SELECT statement to only select movies released after October 31, 2015: SELECT*FROM Movie WHERE ReleaseDate >'2015-10-31'; Then run the SQL again and verify the new query returns only three movies, all with release dates after October 31, 2015. CREATE TABLE Movie ( ID INT, Title VARCHAR(100), Rating VARCHAR(5), ReleaseDate DATE); INSERT INTO Movie VALUES (1, 'Rogue One: A Star Wars Story', 'PG-13', '2016-12-10'), (2, 'Hidden Figures', 'PG', '2017-01-06'), (3, 'Toy Story', 'G', '1995-11-22'), (4, 'Avengers: Endgame', 'PG-13', '2019-04-26'), (5, 'The Godfather', 'R', '1972-03-14'); -- Modify the SELECT statement:SELECT *FROM Movie;Where ReleaseDate > '2015-10-31';arrow_forward
- Write a query in SQL to display all the data of customers, in Table customers, that live in New York or California SELECT city FROM customers WHERE city = 'New York' OR city = 'California' SELECT * FROM customers WHERE city = 'New York' AND city = 'California' SELECT * FROM customers WHERE city = 'New York' OR city = 'California' SELECT ALL FROM customers WHERE city = 'New York' OR city = 'California' %3Darrow_forwardHow do you compose a subquery in SQL where you are searching for the most common value in one column for a specific value from another column (i.e. looking for the down where most penalties occur --> down is a column and PlayType is a column with penalties as a value). The columns are in the same table.arrow_forwardPlease help with pl/sql block!arrow_forward
- Write an SQL query using the NOT operator that will show all employeeinformation from the Employee table with the exception of EmployeeNumber 7344.arrow_forwardWrite an SQL query using the UPDDATE and SET operator that willoverwrite all values containing 16 with 32 in the SupplierID attribute inthe Products table.arrow_forwardWrite a query in SQL code for: "List the book categories and the average book price of each category." Tablename is "BOOKS" and column names are: ISBN TITLE PUBDATE PUBID COST RETAIL DISCOUNT CATEGORYarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education