
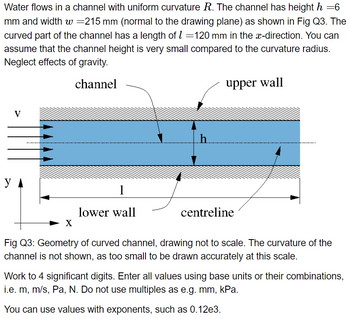
I need help on these questions:
a) Assuming that the pressure is uniform on each of the channel walls, determine the pressure difference between the upper and lower wall that is needed if the required net force on the two walls is 1950N pointing downward (in the negative y-direction). Use a sign convention that a positive pressure difference or gradient means the pressure at the higher y-position is higher.
The value of the pressure difference is ________ Pa.
The value of the pressure gradient across the channel is ________ Pa/m
b) Your team agree that, from experience, the average velocity of the fluid is v=55m/s Assuming that the velocity is uniform across the channel, and neglecting gravitational effects, determine the curvature R required to generate this force with this flow velocity.
Use a sign convention that a positive value indicates that the centre of the radius is above the channel, i.e. the middle of the channel is bent downwards. A negative radius indicates the middle of the channel is bent upwards.
The curvature radius R is __________ m.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Three types of fluids stack in an open tank as shown in the picture. If the specific gravidties are sg1=1.00, sg2=2.00, sg3=3.00, and h1=1.00 m, h2=1.00 m, h3=1.00 m, calculate the gage pressure at location 4, P4(gage)=_________(kPa)arrow_forwardHelp with the correct solution,Show full work.arrow_forwardWater flows in a channel with uniform curvature R. The channel has height h = 6 mm and width w=190 mm (normal to the drawing plane) as shown in Fig Q3. The curved part of the channel has a length of 1 =95 mm in the x-direction. You can assume that the channel height is very small compared to the curvature radius. Neglect effects of gravity. channel y V X 1 lower wall h upper wall centreline Fig Q3: Geometry of curved channel, drawing not to scale. The curvature of the channel is not shown, as too small to be drawn accurately at this scale. Work to 4 significant digits. Enter all values using base units or their combinations, i.e. m, m/s, Pa, N. Do not use multiples as e.g. mm, kPa. You can use values with exponents, such as 0.12e3.arrow_forward
- Don't Use Chat GPT Will Upvotearrow_forward(15 pts) A rectangular gate is installed in a vertical wall of a reservoir, as shown in the figure below. Compute the magnitude of the resultant force on the gate and the location of the center of pressure. 36 ft Latch 4.0 ft Hinge Water Latches Gate -8.0 ftarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





