
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
I have my graph made but need to do the following but do not remember how.
"Use graph paper in lab book to plot moles S2O82- consumed versus time in seconds and fit with a line of best fit."
"To determine the slope of your line do not use any of the data points from your data, use 2 points on your straight line."
"Units of rate are M/s so you must calculate rate from the slope of your line (mol/s)"
The first picture is the graph, using the seconds and moles from the second picture.
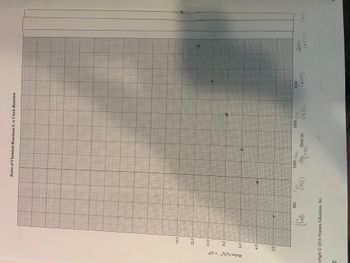
Transcribed Image Text:Moles S₂0² × 104
14.0
12.0
10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
300
500
(349)
pyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
0
Rates of Chemical Reactions I: A Clock Reaction
700
(746)
1000 100
Time (s)
1159)
1500 16,00
(1616)
2000
(2054)
2500
(2545)
(3/10)
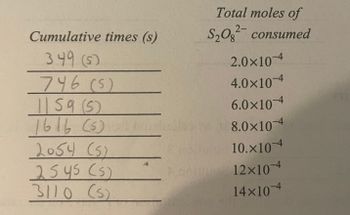
Transcribed Image Text:Cumulative times (s)
349 (5)
746 (5)
|| 59 (5)
1616 (5)
2054 (5)
2545 (5)
3110 (5)
Total moles of
S₂O2 consumed
2.0×10-4
4.0×10-4
6.0×10-4
8.0×10-4
10.x104
12×10-4
14×10-4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemistry graduate student is studying the rate of this reaction: She fills a reaction vessel with and measures its concentration as the reaction proceeds: time (seconds) Use this data to answer the following questions. Write the rate law for this reaction. rate Calculate the value of the rate constant . Round your answer to significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol.arrow_forwardQuestion Use the initial rates method with the given data to determine the rate law for the hypothetical reaction shown below. A+B → C • Write the rate law in the form of rate = k[A]"[B]", specifying the value of the rate constant (k) and the reaction orders (m and n). • Include three significant figures in the rate constant. • Enter your answer in decimal form, do not use scientific notation. Trial [A] (mol/L) [B] (mol/L) 1 2 3 Provide your answer below: rate = 0.0300 0.0300 0.0600 0.0300 0.0600 0.0300 A[A] At (mol L-¹s-¹) 0.0004851 0.0004851 0.0019404arrow_forwardChemistry How can I find the rate orders.arrow_forward
- Here is a graph of the molarity of ammonia (NH,) in a reaction vessel during a certain chemical reaction. Use this graph to answer the questions in the table below. 0.003 0.00213 0.002 0.001 5 10 15 20 25 30 secondsarrow_forwardCalculating the reaction rate of one reactant from that of another Nitric acid is a key industrial chemical, largely used to make fertilizers and explosives. The first step in its synthesis is the oxidation of ammonia. In this reaction, gaseous ammonia reacts with dioxygen gas to produce nitrogen monoxide gas and water. alo Suppose a chemical engineer studying a new catalyst for the oxidation of ammonia reaction finds that 514. liters per second of dioxygen are consumed when the reaction is run at 213. °c and the dioxygen is supplied at 0.64 atm. Calculate the rate at which nitrogen monoxide is being produced. Give your answer in kilograms per second. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Ar kg x10 S ||arrow_forwardIn a study of the conversion of methyl isonitrile to acetonitrile in the gas phase at 250 CH 3 NC(g) CH 3 CN(g) the concentration of CH 3 NC was followed as a function of time It was found that a graph of ln[CH 3 NC] versus time in seconds gave a straight line with a slope of - 4.17 * 10 ^ - 3 * s ^ - 1 and a y intercept of -4.05 Based on this plot , the reaction is order in CH 3 NC and the rate constant for the reaction isarrow_forward
- Can you please help me with this?arrow_forwardlanation M 0.1705 0.15 0.09571 Check 0.05 0 JUL 1011 15 Is C6H12O6 being created or destroyed by the chemical reaction? seconds If C6H12O6 is being created or destroyed, what is the rate at which it is being created or destroyed 11 seconds after the reaction starts? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. If C6H12O6 is being created or destroyed, what is the average rate at which it is being created or destroyed during the first 11 seconds of the reaction? tv 20 25.08 created O destroyed W 30 neither created nor destroyed 00 ☐ X 5 0.0 © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacarrow_forward2. The decomposition reaction of HO2 is given by 4 HO, (g) → 2 H2O (g) + 3 O, (g). From the following kinetics data (concentration of HOz vs. time) and two figures below, answer the following questions. Time (min) [HO;] M (or mol/L) 0.0000 2.0000 1.2500 0.66667 0.5 2.5000 0.40000 3.7500 0.28571 In [ HO, ] 1 5.0000 0.22222 [ HO, 1 4.5 2. The reaction order of HO2 should -1 be order. 1.5 a) Zero-th b) First c) Second time (min) time (min) d) None of the abovearrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardopenvellum ecollege.com/course.html?courseld=16903471&0penvellumHMAC=041020UD6609 TUCTD3247D2609418712#T030T Constants Periodic Table To solve stoichiometry problems, you must always calculate numbers of moles. Recall that molarity, M, is equal to the concentration in moles per liter: M = mol/L. When solutions of silver nitrate and potassium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution according to the equation AGNO3 (aq) + KCI(aq)→AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) Part A What mass of silver chloride can be produced from 1.47 L of a 0.156 M solution of silver nitrate? Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) ? mass of AgCl = Value Units Submit Part B P Pearson Copyright © 2021 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Policy I Permissions I Contact Us I 10:05 acerarrow_forwardWhat percentage of 162X (t1/2 = 401.9 h) would remain after 1,417.3 hours. Use the formula with 0.693 instead of ln 2. The data for element X does not exist. All numbers are hypothetical.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY