
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please answer I,j,and k using excel

Transcribed Image Text:Certainly! Here is the transcription of the text that could appear on an educational website:
---
**Statistical Analysis Exercises**
**i) Compute the error sum of squares**
This step involves calculating the error sum of squares, which is a measure of variability within a data set that cannot be explained by the model. It is calculated by summing the squared differences between observed values and the values predicted by the model.
**j) Compute the total sum of squares**
This involves calculating the total sum of squares, which is the total variation in the data. It is determined by summing the squared differences between each data point and the overall mean of the data set.
**k) Divide the regression sum of squares by the total sum of squares. What is the relationship between this quantity and the correlation coefficient?**
In this exercise, you will calculate the proportion of variance explained by the model by dividing the regression sum of squares by the total sum of squares. This ratio is also known as the coefficient of determination, \( R^2 \), which indicates the strength and direction of the linear relationship between variables. Explore how this relates to the correlation coefficient, which measures the degree of correlation between the predicted and observed values.
---
This transcription aims to provide a comprehensive guide for learners to perform these statistical calculations and understand their implications in data analysis.
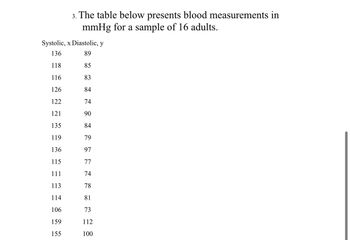
Transcribed Image Text:### Blood Pressure Measurements for a Sample of Adults
The table below presents blood pressure measurements in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) for a sample of 16 adults. Each entry includes both systolic (x) and diastolic (y) values.
| Systolic (x) | Diastolic (y) |
|--------------|--------------|
| 136 | 89 |
| 118 | 85 |
| 116 | 83 |
| 126 | 84 |
| 122 | 74 |
| 121 | 90 |
| 135 | 84 |
| 119 | 79 |
| 136 | 97 |
| 115 | 77 |
| 111 | 74 |
| 113 | 78 |
| 114 | 81 |
| 106 | 73 |
| 159 | 112 |
| 155 | 100 |
This data set provides a snapshot of blood pressure readings, useful for analyzing health trends or correlations between systolic and diastolic values among adults.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman